Page 1777 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1777
1752 Part XI: Malignant Lymphoid Diseases Chapter 107: Myeloma 1753
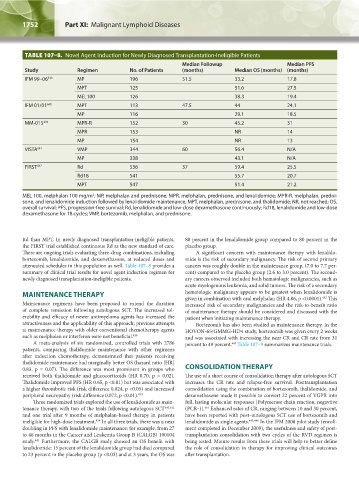
TABLE 107–8. Novel Agent Induction for Newly Diagnosed Transplantation-Ineligible Patients
Median Followup Median PFS
Study Regimen No. of Patients (months) Median OS (months) (months)
IFM 99–06 538 MP 196 51.5 33.2 17.8
MPT 125 51.6 27.5
MEL100 126 38.3 19.4
IFM 01/01 640 MPT 113 47.5 44 24.1
MP 116 29.1 18.5
MM-015 434 MPR-R 152 30 45.2 31
MPR 153 NR 14
MP 154 NR 13
VISTA 641 VMP 344 60 56.4 N/A
MP 338 43.1 N/A
FIRST 437 Rd 536 37 59.4 25.5
Rd18 541 55.7 20.7
MPT 547 51.4 21.2
MEL 100, melphalan 100 mg/m ; MP, melphalan and prednisone; MPR, melphalan, prednisone, and lenalidomide; MPR-R, melphalan, predni-
2
sone, and lenalidomide induction followed by lenalidomide maintenance; MPT, melphalan, prednisone, and thalidomide; NR, not reached; OS,
overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; Rd, lenalidomide and low-dose dexamethasone continuously; Rd18, lenalidomide and low-dose
dexamethasone for 18 cycles; VMP, bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone.
Rd than MPT. In newly diagnosed transplantation-ineligible patients, 88 percent in the lenalidomide group compared to 80 percent in the
the FIRST trial established continuous Rd as the new standard of care. placebo group.
There are ongoing trials evaluating three-drug combinations, including A significant concern with maintenance therapy with lenalido-
bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone, at reduced doses and mide is the risk of secondary malignancy. The risk of second primary
attenuated schedules in this population as well. Table 107–8 provides a cancers was roughly double in the maintenance group, (7.0 to 7.7 per-
summary of clinical trial results for novel agent induction regimen for cent) compared to the placebo group (2.6 to 3.0 percent). The second-
newly diagnosed transplantation-ineligible patients. ary cancers observed included both hematologic malignancies, such as
acute myelogenous leukemia, and solid tumors. The risk of a secondary
MAINTENANCE THERAPY hematologic malignancy appears to be greatest when lenalidomide is
given in combination with oral melphalan (HR 4.86, p <0.0001). This
442
Maintenance regimens have been proposed to extend the duration increased risk of secondary malignancies and the risk-to-benefit ratio
of complete remission following autologous SCT. The increased tol- of maintenance therapy should be considered and discussed with the
erability and efficacy of newer antimyeloma agents has increased the patient when initiating maintenance therapy.
attractiveness and the applicability of this approach; previous attempts Bortezomib has also been studied as maintenance therapy. In the
at maintenance therapy with older conventional chemotherapy agents HOVON-65/GMMG-HD4 study, bortezomib was given every 2 weeks
such as melphalan or interferon were not beneficial. 438 and was associated with increasing the near CR and CR rate from 31
A meta-analysis of six randomized, controlled trials with 2786 percent to 49 percent. Table 107–9 summarizes maintenance trials.
443
patients, comparing thalidomide maintenance with other regimens
after induction chemotherapy, demonstrated that patients receiving
thalidomide maintenance had marginally better OS (hazard ratio [HR]
0.83, p = 0.07). The difference was most prominent in groups who CONSOLIDATION THERAPY
received both thalidomide and glucocorticoids (HR 0.70, p = 0.02). The use of a short course of consolidation therapy after autologous SCT
Thalidomide improved PFS (HR 0.65, p <0.01) but was associated with increases the CR rate and relapse-free survival. Posttransplantation
a higher thrombotic risk (risk difference 0.024, p <0.05) and increased consolidation using the combination of bortezomib, thalidomide, and
peripheral neuropathy (risk difference 0.072, p <0.01). 439 dexamethasone made it possible to convert 22 percent of VGPR into
Three randomized trials explored the use of lenalidomide as main- full, lasting molecular responses [Polymerase chain reaction, negavtive
tenance therapy, with two of the trials following autologous SCT 440,441 (PCR–)]. Enhanced rates of CR, ranging between 10 and 30 percent,
444
and one trial after 9 months of melphalan-based therapy in patients have been reported with post–autologous SCT use of bortezomib and
434
ineligible for high-dose treatment. In all three trials, there was a near lenalidomide as single agents. 445,446 In the IFM 2008 pilot study (enroll-
doubling in PFS with lenalidomide maintenance; for example, from 27 ment completed in December 2009), the usefulness and safety of post-
to 46 months in the Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB) 100104 transplantation consolidation with two cycles of the RVD regimen is
study. Furthermore, the CALGB study showed an OS benefit with being tested. Mature results from these trials will help to better define
441
lenalidomide: 15 percent of the lenalidomide group had died compared the role of consolidation in therapy for improving clinical outcomes
to 23 percent in the placebo group (p <0.03) and at 3 years, the OS was after transplantation.
Kaushansky_chapter 107_p1733-1772.indd 1752 9/21/15 12:35 PM