Page 1857 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1857
1832 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 112: Platelet Morphology, Biochemistry, and Function 1833
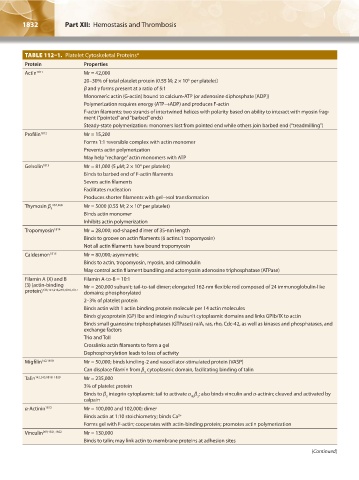
TABLE 112–1. Platelet Cytoskeletal Proteins*
Protein Properties
Actin 1811 Mr = 42,000
20–30% of total platelet protein (0.55 M; 2 × 10 per platelet)
6
β and γ forms present at a ratio of 5:1
Monomeric actin (G-actin) bound to calcium-ATP (or adenosine diphosphate [ADP])
Polymerization requires energy (ATP→ADP) and produces F-actin
F-actin filaments: two strands of intertwined helices with polarity based on ability to interact with myosin frag-
ment (“pointed” and “barbed” ends)
Steady-state polymerization: monomers lost from pointed end while others join barbed end (“treadmilling”)
Profilin 1812 Mr = 15,200
Forms 1:1 reversible complex with actin monomer
Prevents actin polymerization
May help “recharge” actin monomers with ATP
Gelsolin 1813 Mr = 81,000 (5 μM; 2 × 10 per platelet)
4
Binds to barbed end of F-actin filaments
Severs actin filaments
Facilitates nucleation
Produces shorter filaments with gel→sol transformation
6
Thymosin β 267,268 Mr = 5000 (0.55 M; 2 × 10 per platelet)
4
Binds actin monomer
Inhibits actin polymerization
Tropomyosin 1814 Mr = 28,000; rod-shaped dimer of 35-nm length
Binds to groove on actin filaments (6 actins:1 tropomyosin)
Not all actin filaments have bound tropomyosin
Caldesmon 1815 Mr = 80,000; asymmetric
Binds to actin, tropomyosin, myosin, and calmodulin
May control actin filament bundling and actomyosin adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase)
Filamin A (X) and B Filamin A-to-B = 10:1
(3) (actin-binding Mr = 260,000 subunit; tail-to-tail dimer; elongated 162-nm flexible rod composed of 24 immunoglobulin-like
protein) 133,154,216,249,1816,1817 domains; phosphorylated
2–3% of platelet protein
Binds actin with 1 actin binding protein molecule per 14 actin molecules
Binds glycoprotein (GP) Ibα and integrin β subunit cytoplasmic domains and links GPIb/IX to actin
Binds small guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases) ralA, ras, rho, Cdc-42, as well as kinases and phosphatases, and
exchange factors
Trio and Toll
Crosslinks actin filaments to form a gel
Dephosphorylation leads to loss of activity
Migfilin 142,1818 Mr = 50,000; binds kindling-2 and vasodilator-stimulated protein (VASP)
Can displace filamin from β cytoplasmic domain, facilitating binding of talin
3
Talin 142,245,1818–1820 Mr = 235,000
3% of platelet protein
Binds to β integrin cytoplasmic tail to activate α β ; also binds vinculin and α-actinin; cleaved and activated by
3
IIb 3
calpain
α-Actinin 1812 Mr = 100,000 and 102,000; dimer
Binds actin at 1:10 stoichiometry; binds Ca 2+
Forms gel with F-actin; cooperates with actin-binding protein; promotes actin polymerization
Vinculin 269,1821,1822 Mr = 130,000
Binds to talin; may link actin to membrane proteins at adhesion sites
(Continued)
Kaushansky_chapter 112_p1829-1914.indd 1832 17/09/15 3:25 pm