Page 2140 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 2140
2114 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 123: Hemophilia A and Hemophilia B 2115
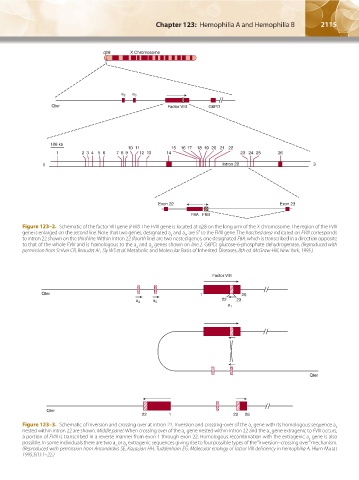
q28 X Chromosome
a 2 a 3
Qter Factor VIII G6PD
186 kb
10 11 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 89 12 13 14 23 24 25 26
5 Intron 22 3
Exon 22 Exon 23
F8A F8B
Figure 123–2. Schematic of the factor VIII gene (FVIII). The FVIII gene is located at q28 on the long arm of the X chromosome. The region of the FVIII
gene is enlarged on the second line. Note that two genes, designated a and a , are 5′ to the FVIII gene. The hatched area indicated on FVIII corresponds
2
3
to intron 22 shown on the third line. Within intron 22 (fourth line) are two nested genes, one designated F8A, which is transcribed in a direction opposite
to that of the whole FVIII and is homologous to the a and a genes shown on line 2. G6PD, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. (Reproduced with
2
3
permission from Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS et al: Metabolic and Molecular Basis of Inherited Diseases, 8th ed. McGraw-Hill, New York, 1995.)
Factor VIII
Qter 1 26
22 23
a 3 a 2
a 1
Qter
Qter
22 1 23 26
Figure 123–3. Schematic of inversion and crossing over at intron 22. Inversion and crossing-over of the a gene with its homologous sequence a
1
3
nested within intron 22 are shown. Middle panel: When crossing over of the a gene nested within intron 22 and the a gene extragenic to FVIII occurs,
3
1
a portion of FVIII is transcribed in a reverse manner from exon 1 through exon 22. Homologous recombination with the extragenic a gene is also
2
possible. In some individuals there are two a or a extragenic sequences giving rise to four possible types of the “inversion–crossing over” mechanism.
2
3
(Reproduced with permission from Antonarakis SE, Kazazian HH, Tuddenham EG: Molecular etiology of factor VIII deficiency in hemophilia A. Hum Mutat
1995;5(1):1–22.)
Kaushansky_chapter 123_p2113-2132.indd 2115 9/21/15 4:35 PM