Page 247 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 247
222 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 16: Cell-Cycle Regulation and Hematologic Disorders 223
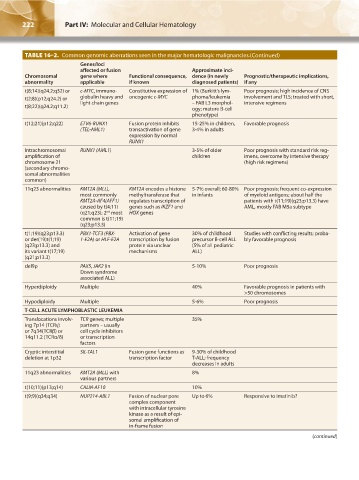
TABLE 16–2. Common genomic aberrations seen in the major hematologic malignancies.(Continued)
Genes/loci
affected or fusion Approximate inci-
Chromosomal gene where Functional consequence, dence (in newly Prognostic/therapeutic implications,
abnormality applicable if known diagnosed patients) if any
t(8;14)(q24.2;q32) or c-MYC, immuno- Constitutive expression of 1% (Burkitt’s lym- Poor prognosis; high incidence of CNS
t(2;8)(p12;q24.2) or globulin heavy and oncogenic c-MYC phoma/leukemia involvement and TLS; treated with short,
t(8;22)(q24.2;q11.2) light chain genes – FAB L3 morphol- intensive regimens
ogy; mature B-cell
phenotype)
t(12;21)(p12;q22) ETV6-RUNX1 Fusion protein inhibits 15-25% in children, Favorable prognosis
(TEL-AML1) transactivation of gene 3-4% in adults
expression by normal
RUNX1
Intrachromosomal RUNX1 (AML1) 3-5% of older Poor prognosis with standard risk reg-
amplification of children imens, overcome by intensive therapy
chromosome 21 (high risk regimens)
(secondary chromo-
somal abnormalities
common)
11q23 abnormalities KMT2A (MLL), KMT2A encodes a histone 5-7% overall; 60-80% Poor prognosis; frequent co-expression
most commonly methyltransferase that in infants of myeloid antigens; about half the
KMT2A-AF4(AFF1) regulates transcription of patients with t(11;19)(q23;p13.3) have
caused by t(4;11) genes such as IKZF1 and AML, mostly FAB M5a subtype
(q21;q23); 2 most HOX genes
nd
common is t(11;19)
(q23;p13.3)
t(1;19)(q23;p13.3) PBX1-TCF3 (PBX- Activation of gene 30% of childhood Studies with conflicting results; proba-
or der(19)t(1;19) 1-E2A) or HLF-E2A transcription by fusion precursor B-cell ALL bly favorable prognosis
(q23;p13.3) and protein via unclear (5% of all pediatric
its variant t(17;19) mechanisms ALL)
(q21;p13.3)
del9p PAX5, JAK2 (in 5-10% Poor prognosis
Down syndrome
associated ALL)
Hyperdiploidy Multiple 40% Favorable prognosis in patients with
>50 chromosomes
Hypodiploidy Multiple 5-6% Poor prognosis
T-CELL ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA
Translocations involv- TCR genes; multiple 35%
ing 7p14 (TCRγ) partners – usually
or 7q34(TCRβ) or cell cycle inhibitors
14q11.2 (TCRα/δ) or transcription
factors
Cryptic interstitial SIL-TAL1 Fusion gene functions as 9-30% of childhood
deletion at 1p32 transcription factor T-ALL; frequency
decreases in adults
11q23 abnormalities KMT2A (MLL) with 8%
various partners
t(10;11)(p13;q14) CALM-AF10 10%
t(9;9)(q34;q34) NUP214-ABL1 Fusion of nuclear pore Up to 6% Responsive to imatinib?
complex component
with intracellular tyrosine
kinase as a result of epi-
somal amplification of
in-frame fusion
(continued)
Kaushansky_chapter 16_p0213-0246.indd 222 9/18/15 11:57 PM