Page 245 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 245
220 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 16: Cell-Cycle Regulation and Hematologic Disorders 221
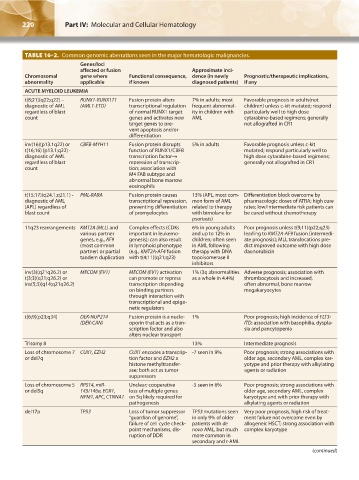
TABLE 16–2. Common genomic aberrations seen in the major hematologic malignancies.
Genes/loci
affected or fusion Approximate inci-
Chromosomal gene where Functional consequence, dence (in newly Prognostic/therapeutic implications,
abnormality applicable if known diagnosed patients) if any
ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA
t(8;21)(q22;q22) – RUNX1-RUNX1T1 Fusion protein alters 7% in adults; most Favorable prognosis in adults(not
diagnostic of AML (AML1-ETO) transcriptional regulation frequent abnormal- children) unless c-kit mutated; respond
regardless of blast of normal RUNX1 target ity in children with particularly well to high dose
count genes and activates new AML cytarabine-based regimens; generally
target genes to pre- not allografted in CR1
vent apoptosis and/or
differentiation
inv(16)(p13.1q22) or CBFB-MYH11 Fusion protein disrupts 5% in adults Favorable prognosis unless c-kit
t(16;16) (p13.1;q22) - function of RUNX1/CBFB mutated; respond particularly well to
diagnostic of AML transcription factor→ high dose cytarabine-based regimens;
regardless of blast repression of transcrip- generally not allografted in CR1
count tion; association with
M4 FAB subtype and
abnormal bone marrow
eosinophils
t(15;17)(q24.1;q21.1) - PML-RARA Fusion protein causes 13% (APL, most com- Differentiation block overcome by
diagnostic of AML transcriptional repression, mon form of AML pharmacologic doses of ATRA; high cure
(APL) regardless of preventing differentiation related to therapy rates; low/intermediate risk patients can
blast count of promyelocytes with bimolane for be cured without chemotherapy
psoriasis)
11q23 rearrangements KMT2A (MLL) and Complex effects (CDKs 6% in young adults Poor prognosis unless t(9;11)(p22;q23)
various partner important in leukemo- and up to 12% in leading to KMT2A-AF9 fusion (intermedi-
genes, e.g., AF9 genesis); can also result children; often seen ate prognosis); MLL translocations pre-
(most common in lymphoid phenotype in AML following dict improved outcome with high dose
partner) or partial (e.g., KMT2A-AF4 fusion therapy with DNA daunorubicin
tandem duplication with t(4;11)(q21;q23) topoisomerase II
inhibitors
inv(3)(q21q26.2) or MECOM (EV1) MECOM (EV1) activation 1% (3q abnormalities Adverse prognosis; association with
t(3;3)(q21;q26.2) or can promote or repress as a whole in 4.4%) thrombocytosis and increased,
ins(5;3)(q14;q21q26.2) transcription depending often abnormal, bone marrow
on binding partners megakaryocytes
through interaction with
transcriptional and epige-
netic regulators
t(6;9)(p23;q34) DEK-NUP214 Fusion protein is a nucle- 1% Poor prognosis; high incidence of FLT3-
(DEK-CAN) oporin that acts as a tran- ITD; association with basophilia, dyspla-
scription factor and also sia and pancytopenia
alters nuclear transport
Trisomy 8 13% Intermediate prognosis
Loss of chromosome 7 CUX1, EZH2 CUX1 encodes a transcrip- -7 seen in 9% Poor prognosis; strong associations with
or del7q tion factor and EZH2 a older age, secondary AML, complex kar-
histone methyltransfer- yotype and prior therapy with alkylating
ase; both act as tumor agents or radiation
suppressors
Loss of chromosome 5 RPS14, miR- Unclear; cooperative -5 seen in 6% Poor prognosis; strong associations with
or del5q 145/146a, EGR1, loss of multiple genes older age, secondary AML, complex
NPM1, APC, CTNNA1 on 5q likely required for karyotype and with prior therapy with
pathogenesis alkylating agents or radiation
del17p TP53 Loss of tumor suppressor TP53 mutations seen Very poor prognosis, high risk of treat-
“guardian of genome”, in only 9% of older ment failure not overcome even by
failure of cell cycle check- patients with de allogeneic HSCT; strong association with
point mechanisms, dis- novo AML, but much complex karyotype
ruption of DDR more common in
secondary and t-AML
(continued)
Kaushansky_chapter 16_p0213-0246.indd 220 9/18/15 11:57 PM