Page 246 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 246
220 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 16: Cell-Cycle Regulation and Hematologic Disorders 221
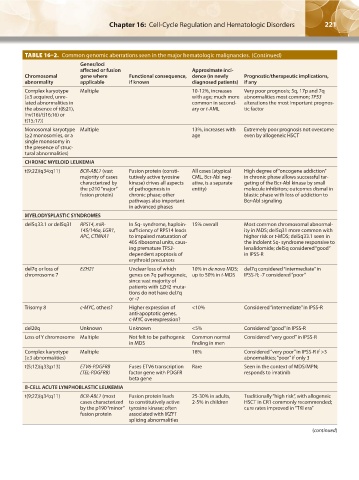
TABLE 16–2. Common genomic aberrations seen in the major hematologic malignancies. (Continued)
Genes/loci
affected or fusion Approximate inci-
Chromosomal gene where Functional consequence, dence (in newly Prognostic/therapeutic implications,
abnormality applicable if known diagnosed patients) if any
Complex karyotype Multiple 10-12%, increases Very poor prognosis; 5q, 17p and 7q
(≥3 acquired, unre- with age; much more abnormalities most common; TP53
lated abnormalities in common in second- alterations the most important prognos-
the absence of t(8;21), ary or t-AML tic factor
inv(16)/t(16;16) or
t(15;17))
Monosomal karyotype Multiple 13%, increases with Extremely poor prognosis not overcome
(≥2 monosomies, or a age even by allogeneic HSCT
single monosomy in
the presence of struc-
tural abnormalities)
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
t(9;22)(q34;q11) BCR-ABL1 (vast Fusion protein (consti- All cases (atypical High degree of “oncogene addiction”
majority of cases tutively active tyrosine CML, Bcr-Abl neg- in chronic phase allows successful tar-
characterized by kinase) drives all aspects ative, is a separate geting of the Bcr-Abl kinase by small
the p210 “major” of pathogenesis in entity) molecule inhibitors; outcomes dismal in
fusion protein) chronic phase; other blastic phase with loss of addiction to
pathways also important Bcr-Abl signaling
in advanced phases
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES
del5q33.1 or del5q31 RPS14, miR- In 5q- syndrome, haploin- 15% overall Most common chromosomal abnormal-
145/146a, EGR1, sufficiency of RPS14 leads ity in MDS; del5q31 more common with
APC, CTNNA1 to impaired maturation of higher risk or t-MDS; del5q33.1 seen in
40S ribosomal units, caus- the indolent 5q- syndrome responsive to
ing premature TP53- lenalidomide; del5q considered “good”
dependent apoptosis of in IPSS-R
erythroid precursors
del7q or loss of EZH2? Unclear loss of which 10% in de novo MDS; del7q considered “intermediate” in
chromosome 7 genes on 7q pathogeneic, up to 50% in t-MDS IPSS-R; -7 considered “poor”
since vast majority of
patients with EZH2 muta-
tions do not have del7q
or -7
Trisomy 8 c-MYC, others? Higher expression of <10% Considered “intermediate” in IPSS-R
anti-apoptotic genes,
c-MYC overexpression?
del20q Unknown Unknown <5% Considered “good” in IPSS-R
Loss of Y chromosome Multiple Not felt to be pathogenic Common normal Considered “very good” in IPSS-R
in MDS finding in men
Complex karyotype Multiple 18% Considered “very poor” in IPSS-R if >3
(≥3 abnormalities) abnormalities; “poor” if only 3
t(5;12)(q33;p13) ETV6-PDGFRB Fuses ETV6 transcription Rare Seen in the context of MDS/MPN;
(TEL-PDGFRB) factor gene with PDGFR responds to imatinib
beta gene
B-CELL ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA
t(9;22)(q34;q11) BCR-ABL1 (most Fusion protein leads 25-30% in adults, Traditionally “high risk”, with allogeneic
cases characterized to constitutively active 2-5% in children HSCT in CR1 commonly recommended;
by the p190 “minor” tyrosine kinase; often cure rates improved in “TKI era”
fusion protein associated with IKZF1
splicing abnormalities
(continued)
Kaushansky_chapter 16_p0213-0246.indd 221 9/18/15 11:57 PM