Page 314 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 314
288 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 19: The Inflammatory Response 289
of the lipoxygenase pathway results in the synthesis of 5-hydroperox- factor (factor XIIa), also known as the prekallikrein activator, converts
yeicosatetraenoic acid (5-HPETE), which is a potent chemoattractant plasma prekallikrein to kallikrein. In turn, kallikrein cleaves high-
of neutrophils and can be enzymatically modified to yield a series of molecular-weight kininogen to produce bradykinin. Models of septic
other leukotrienes. LTB induces neutrophil chemotaxis, aggregation, shock reveal decreases in plasma kininogen that parallel decreases in
4
degranulation, and adherence, while LTC , LTD , and LTE trigger peripheral arterial resistance. 44
4
4
4
smooth-muscle constriction, increases in vascular permeability and
41
bronchoconstriction. Members of both of these families of lipid- VASOACTIVE AMINES
derived mediators and their catabolites have been detected in inflamma-
tory exudates. There are two important branches within the lipoxygenase Histamine and serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) are low-molecular-
pathway. 41,42 Lipoxins (A [LXA ] and B [LXB ]) are generated via the weight vasoactive amines. Histamine is contained in mast cell and
4
4
4
4
45
12-lipooxygenase branch of the lipoxygenase pathway in conjunction basophil granules, whereas platelets are a chief source of serotonin.
with a unique transcellular biosynthetic pathway. Neutrophils gener- Localized release of histamine results in wheal formation as a conse-
42
ate LTA via the 5-lipoxygenase pathway branch; in turn, lipoxins (LXA quence of increases in vascular permeability. Histamine induces the
4
4
and LXB ) are generated through the action of platelet 12-lipooxygense formation of reversible openings in endothelial tight junctions, trig-
4
on neutrophil LTA . Prevention of neutrophil-platelet binding interrupts gers the formation of prostacyclin by endothelial cells and induces NO
4
this pathway. Lipoxins inhibit neutrophil chemotaxis and adhesion to release from the endothelium. In addition, histamine, like thrombin,
45
42
endothelium. As noted above, resolvins and protectins each encompass can induce the rapid upregulation of endothelial P-selectin. Serotonin,
several molecular species—all derived from omega-3 polyunsaturated acting through receptors on vascular smooth-muscle cells, is responsi-
fatty acids. 26,27 ble for vasoconstriction, whereas interaction with endothelial receptors
2
PAF is a potent proinflammatory lipid produced by a variety of results in vasodilation (via release of NO) and increased permeability.
cell types, including neutrophils, monocytes, endothelial cells and IgE- Release of histamine and serotonin from mast cells and platelets can
sensitized basophils. Derived from the cell membrane constituent, be triggered by IgE-mediated type I hypersensitivity reactions, directly
43
choline phosphoglyceride, PAF is an acetyl glycerol ether phosphocho- by C3a or C5a, and directly by neutrophil granule-derived cationic
line that is synthesized following the activation of phospholipase A . proteins.
2
PAF triggers platelet aggregation and degranulation, increases vascular
permeability, and promotes leukocyte accumulation and activation. In
vivo studies using specific PAF antagonists have suggested a role for PAF COMPLEMENT
in a variety of acute inflammatory lesions. 43 The complement system, including its soluble and cell membrane-
associated regulators, consists of nearly two dozen plasma proteins that
KININS give rise to mediators of chemotaxis, increased vascular permeability,
opsonic activity, phagocyte activation, and cytolysis. In a manner
46
The kinin system is activated by contact activation of clotting factor analogous to coagulation, the complement system is activated through
XII (Hageman factor) (Chaps. 113 and 114). Activation of the kinin a cascade of proteolytic cleavage reactions. There are three convergent
44
system results in the generation of bradykinin, a nine-amino-acid pathways (Fig. 19–3). The first of these, the “classical pathway,” is ini-
vasoactive peptide. Bradykinin possesses several activities, including tiated primarily (but not exclusively) by complement-fixing immune
the capacity to increase vascular permeability, induce smooth-muscle complexes (IgG subclasses 1 to 3 and IgM), whereas the second, the
contraction, trigger vasodilation, and cause pain. Activated Hageman “alternative pathway,” is triggered by a variety of substances that include
44
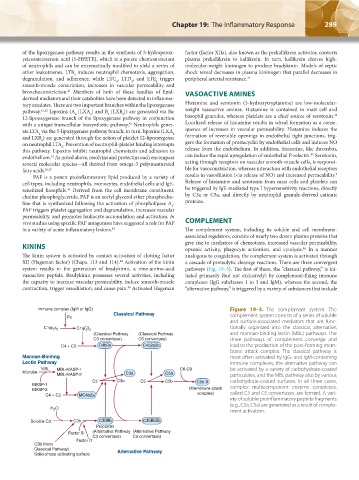
Immune complex (IgM or IgG) Figure 19–3. The complement system. The
Classical Pathway complement system consists of a series of soluble
Fc
and surface-associated mediators that are func-
s tionally organized into the classical, alternative,
C1qr 2 2 C1qr s
2 2
(Classical Pathway (Classical Pathway and mannan-binding lectin (MBL) pathways. The
C3 convertase) C5 convertase) three pathways of complement converge and
C4 + C2 C4b2a C4b2a3b lead to the production of the pore-forming mem-
brane attack complex. The classical pathway is
Mannan-Binding most often activated by IgG- and IgM-containing
Lectin Pathway immune complexes, the alternative pathway can
MBL MBL-MASP-1 C6-C9 be activated by a variety of carbohydrate-coated
Microbe C3a C5a
MBL-MASP-2 particulates, and the MBL pathway also by various
C3 C3b C5 C5b C5b-9 carbohydrate-coated surfaces. In all three cases,
MASP-1 complex multicomponent enzyme complexes,
MASP-2 (Membrane attack
C4 + C2 MC4b2a complex) called C3 and C5 convertases, are formed. A vari-
ety of soluble proinflammatory peptide fragments
(e.g., C3a, C5a) are generated as a result of comple-
H 2 O
ment activation.
Soluble C3 C3b C3bBb C3bBb3b
Properdin
Factor B (Alternative Pathway (Alternative Pathway
C3 convertase) C5 convertase)
Factor D
C3b (from
Classical Pathway) Alternative Pathway
Solid-phase activating surface
Kaushansky_chapter 19_p0279-0292.indd 289 9/17/15 5:51 PM