Page 754 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 754
728 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 48: The Thalassemias: Disorders of Globin Synthesis 729
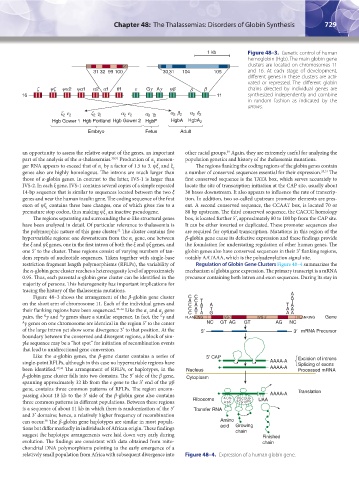
Figure 48–3. Genetic control of human
hemoglobin (Hgb). The main globin gene
clusters are located on chromosomes 11
and 16. At each stage of development,
different genes in these clusters are acti-
vated or repressed. The different globin
chains directed by individual genes are
synthesized independently and combine
in random fashion as indicated by the
arrows.
39
an opportunity to assess the relative output of the genes, an important other racial groups. Again, they are extremely useful for analyzing the
part of the analysis of the α-thalassemias. 30,31 Production of α messen- population genetics and history of the thalassemia mutations.
2
ger RNA appears to exceed that of α by a factor of 1.5 to 3. ψξ and ξ The regions flanking the coding regions of the globin genes contain
1
2
1
genes also are highly homologous. The introns are much larger than a number of conserved sequences essential for their expression. 28,33 The
those of α-globin genes. In contrast to the latter, IVS-1 is larger than first conserved sequence is the TATA box, which serves accurately to
IVS-2. In each ξ gene, IVS-1 contains several copies of a simple repeated locate the site of transcription initiation at the CAP site, usually about
14-bp sequence that is similar to sequences located between the two ξ 30 bases downstream. It also appears to influence the rate of transcrip-
genes and near the human insulin gene. The coding sequence of the first tion. In addition, two so-called upstream promoter elements are pres-
exon of ψξ contains three base changes, one of which gives rise to a ent. A second conserved sequence, the CCAAT box, is located 70 or
1
premature stop codon, thus making ψξ an inactive pseudogene. 80 bp upstream. The third conserved sequence, the CACCC homology
1
The regions separating and surrounding the α-like structural genes box, is located further 5′, approximately 80 to 100 bp from the CAP site.
have been analyzed in detail. Of particular relevance to thalassemia is It can be either inverted or duplicated. These promoter sequences also
the polymorphic nature of this gene cluster. The cluster contains five are required for optimal transcription. Mutations in this region of the
32
hypervariable regions: one downstream from the α gene, one between β-globin gene cause its defective expression and these findings provide
1
the ξ and ψξ genes, one in the first intron of both the ξ and ψξ genes, and the foundation for understating regulation of other human genes. The
one 5′ to the cluster. These regions consist of varying numbers of tan- globin genes also have conserved sequences in their 3′ flanking regions,
dem repeats of nucleotide sequences. Taken together with single-base notably AATAAA, which is the polyadenylation signal site.
restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs), the variability of Regulation of Globin Gene Clusters Figure 48–4 summarizes the
the α-globin gene cluster reaches a heterozygosity level of approximately mechanism of globin gene expression. The primary transcript is a mRNA
0.95. Thus, each parental α-globin gene cluster can be identified in the precursor containing both intron and exon sequences. During its stay in
majority of persons. This heterogeneity has important implications for
tracing the history of the thalassemia mutations.
Figure 48–3 shows the arrangement of the β-globin gene cluster C C A
A
T
on the short arm of chromosome 11. Each of the individual genes and A C T A T A
C A A
their flanking regions have been sequenced. 33–36 Like the α and α gene C A T T A A
C T A
A A
G
1
2
pairs, the γ and γ genes share a similar sequence. In fact, the γ and FLANKING IVS-1 IVS-2 FLANKING Gene
G
A
G
A γ genes on one chromosome are identical in the region 5′ to the center NC GT AG GT AG NC
of the large intron yet show some divergence 3′ to that position. At the 5′ 3′ mRNA Precursor
boundary between the conserved and divergent regions, a block of sim-
ple sequence may be a “hot spot” for initiation of recombination events
that lead to unidirectional gene conversion.
Like the α-globin genes, the β-gene cluster contains a series of 5′ CAP Excision of introns
single-point RFLPs, although in this case no hypervariable regions have AAAA-A Splicing of exons
been identified. 37,38 The arrangement of RFLPs, or haplotypes, in the Nucleus AAAA-A Processed mRNA
β-globin gene cluster falls into two domains. The 5′ side of the β gene, Cytoplasm
spanning approximately 32 kb from the ε gene to the 3′ end of the ψβ
gene, contains three common patterns of RFLPs. The region encom- Translation
passing about 18 kb to the 3′ side of the β-globin gene also contains A U G AAAA-A
U GC
three common patterns in different populations. Between these regions Ribosome U AC A C G UUC UAA
AAG
is a sequence of about 11 kb in which there is randomization of the 5′ Transfer RNA
and 3′ domains; hence, a relatively higher frequency of recombination
can occur. The β-globin gene haplotypes are similar in most popula- Amino
38
tions but differ markedly in individuals of African origin. These findings acid Growing
suggest the haplotype arrangements were laid down very early during chain Finished
evolution. The findings are consistent with data obtained from mito- chain
chondrial DNA polymorphisms pointing to the early emergence of a
relatively small population from Africa with subsequent divergence into Figure 48–4. Expression of a human globin gene.
Kaushansky_chapter 48_p0725-0758.indd 729 9/18/15 2:57 PM