Page 959 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 959
934 Part VII: Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Basophils, and Mast Cells Chapter 60: Structure and Composition of Neutrophils, Eosinophils, and Basophils 935
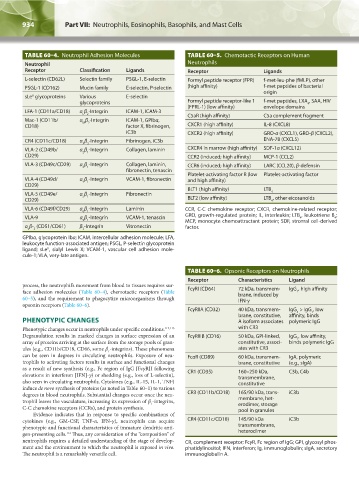
TABLE 60–4. Neutrophil Adhesion Molecules TABLE 60–5. Chemotactic Receptors on Human
Neutrophil Neutrophils
Receptor Classification Ligands Receptor Ligands
L-selectin (CD62L) Selectin family PSGL-1, E-selectin Formyl peptide receptor (FPR) f-met-leu-phe (fMLP), other
PSGL-1 (CD162) Mucin family E-selectin, P-selectin (high affinity) f-met peptides of bacterial
origin
sLe glycoproteins Various E-selectin
X
glycoproteins Formyl peptide receptor-like 1 f-met peptides, LXA , SAA, HIV
4
(FPRL-1) (low affinity) envelope domains
LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18) α β -Integrin ICAM-1, ICAM-3
L 2 C5aR (high affinity) C5a complement fragment
Mac-1 (CD11b/ α β -Integrin ICAM-1, GPIbα,
M 2
CD18) factor X, fibrinogen, CXCR1 (high affinity) IL-8 (CXCL8)
iC3b CXCR2 (high affinity) GRO-α (CXCL1), GRO-β (CXCL2),
CR4 (CD11c/CD18) α β -Integrin Fibrinogen, iC3b ENA-78 (CXCL5)
X 2
VLA-2 (CD49b/ α β -Integrin Collagen, laminin CXCR4 in marrow (high affinity) SDF-1α (CXCL12)
2 1
CD29) CCR2 (induced; high affinity) MCP-1 (CCL2)
VLA-3 (CD49c/CD29) α β -Integrin Collagen, laminin, CCR6 (induced; high affinity) LARC (CCL20), β-defensin
3 1
fibronectin, tenascin
Platelet-activating factor R (low Platelet-activating factor
VLA-4 (CD49d/ α β -Integrin VCAM-1, fibronectin and high affinity)
4 1
CD29)
BLT1 (high affinity) LTB
VLA-5 (CD49e/ α β -Integrin Fibronectin 4
5 1
CD29) BLT2 (low affinity) LTB , other eicosanoids
4
VLA-6 (CD49f/CD29) α β -Integrin Laminin CCR, C-C chemokine receptor; CXCR, chemokine-related receptor;
6 1
VLA-9 α β -Integrin VCAM-1, tenascin GRO, growth-regulated protein; IL, interleukin; LTB , leukotriene B ;
4
4
9 1 MCP, monocyte chemoattractant protein; SDF, stromal cell-derived
α β- (CD51/CD61) β -Integrin Vitronectin factor.
v 3 3
GPIbα, glycoprotein Ibα; ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule; LFA,
leukocyte function-associated antigen; PSGL, P-selectin glycoprotein
ligand; sLe , sialyl Lewis X; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion mole-
X
cule-1; VLA, very-late antigen.
TABLE 60–6. Opsonic Receptors on Neutrophils
Receptor Characteristics Ligand
process, the neutrophil’s movement from blood to tissues requires sur-
face adhesion molecules (Table 60–4), chemotactic receptors (Table FcγRI (CD64) 72 kDa, transmem- IgG , high affinity
1
brane, induced by
60–5), and the requirement to phagocytize microorganisms through IFN-γ
opsonin receptors (Table 60–6).
FcγRIIA (CD32) 40 kDa, transmem- IgG > IgG , low
3
1
brane, constitutive, affinity, binds
PHENOTYPIC CHANGES A isoform associates polymeric IgG
Phenotypic changes occur in neutrophils under specific conditions. 112,113 with CR3
Degranulation results in marked changes in surface expression of an FcγRIIIB (CD16) 50 kDa, GPI-linked, IgG , low affinity,
1
array of proteins arriving at the surface from the storage pools of gran- constitutive, associ- binds polymeric IgG
ules (e.g., CD11b/CD18, CD66, some β -integrins). These phenomena ates with CR3
1
can be seen in degrees in circulating neutrophils. Exposure of neu- FcαR (CD89) 60 kDa, transmem- IgA, polymeric
trophils to activating factors results in surface and functional changes brane, constitutive (e.g., sIgA)
as a result of new synthesis (e.g., Fc region of IgG [FcγR]I following CR1 (CD35) 160–250 kDa, C3b, C4b
elevations in interferon [IFN]-γ) or shedding (e.g., loss of L-selectin), transmembrane,
also seen in circulating neutrophils. Cytokines (e.g., IL-15, IL-1, TNF) constitutive
induce de novo synthesis of proteins (as noted in Table 60–1) to various
degrees in blood neutrophils. Substantial changes occur once the neu- CR3 (CD11b/CD18) 165/90 kDa, trans- iC3b
trophil leaves the vasculature, increasing its expression of β -integrins, membrane, het-
erodimer, storage
1
C-C chemokine receptors (CCRs), and protein synthesis. pool in granules
Evidence indicates that in response to specific combinations of
cytokines (e.g., GM-CSF, TNF-α, IFN-γ), neutrophils can acquire CR4 (CD11c/CD18) 145/90 kDa iC3b
phenotypic and functional characteristics of immature dendritic anti- transmembrane,
112
gen-presenting cells. Thus, any consideration of the “composition” of heterodimer
neutrophils requires a detailed understanding of the stage of develop- CR, complement receptor; FcγR, Fc region of IgG; GPI, glycosyl phos-
ment and the environment to which the neutrophil is exposed in vivo. phatidylinositol; IFN, interferon; Ig, immunoglobulin; sIgA, secretory
The neutrophil is a remarkably versatile cell. immunoglobulin A.
Kaushansky_chapter 60_p0923-0938.indd 934 9/18/15 10:35 PM