Page 1092 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1092
1056 ParT EighT Immunology of Neoplasia
-4
Since leukemia is clonal (i.e., it originates from one lymphoid of leukemic blasts to below 10 cells within the first 2–4 weeks
cell), all of the leukemic cells of a particular person carry the of therapy is detected in ≈40% of children with ALL and is
same Ig and/or TCR rearrangements. Because leukemic cells are associated with an extremely good prognosis. Conversely, the
genetically unstable, they often (>90% of the cases) carry multiple presence of >0.1% blasts after 2 or 3 months of therapy defines
rearrangements, a fact that facilitates the usefulness of using a very-high-risk group. These initial findings have led the BFM-
these rearrangements as a clonal marker for MRD detection. AEIOP study group to initiate a prospective study on children
The major advantages of this technique are the exquisite sensitivity with ALL that utilize the MRD level determined by Ig/TCR-PCR
-5
(at least 10 ), reliability, reproducibility, and its applicability to for risk classification. This study, which involved 3184 patients,
>90% of children with ALL. The application of NGS techniques confirmed the strength of PCR MRD over genetic classification
17
is likely to lower the costs and complexity of this approach. as a prognostic marker. At present, MRD studies have been
Current strategies for flow cytometric detection of MRD rely incorporated into most treatment protocols. Patients with high
on combinations of leukocyte markers that do not normally MRD are stratified into a high-risk arm and receive more intensive
occur in cells of the peripheral blood and bone marrow. Such chemotherapy.
leukemia-associated phenotypes can be identified by multiple
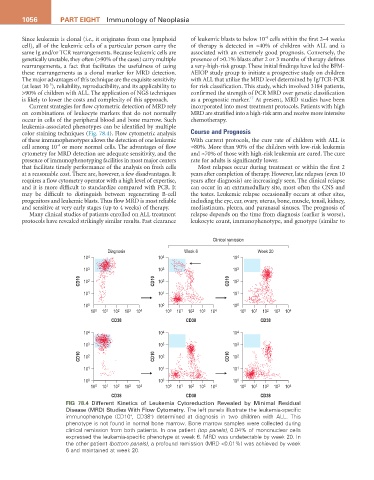
color staining techniques (Fig. 78.4). Flow cytometric analysis Course and Prognosis
of these immunophenotypes allows the detection of one leukemic With current protocols, the cure rate of children with ALL is
-4
cell among 10 or more normal cells. The advantages of flow ≈80%. More than 90% of the children with low-risk leukemia
cytometry for MRD detection are adequate sensitivity, and the and ≈70% of those with high-risk leukemia are cured. The cure
presence of immunophenotyping facilities in most major centers rate for adults is significantly lower.
that facilitate timely performance of the analysis on fresh cells Most relapses occur during treatment or within the first 2
at a reasonable cost. There are, however, a few disadvantages. It years after completion of therapy. However, late relapses (even 10
requires a flow cytometry operator with a high level of expertise, years after diagnosis) are increasingly seen. The clinical relapse
and it is more difficult to standardize compared with PCR. It can occur in an extramedullary site, most often the CNS and
may be difficult to distinguish between regenerating B-cell the testes. Leukemic relapse occasionally occurs at other sites,
progenitors and leukemic blasts. Thus flow MRD is most reliable including the eye, ear, ovary, uterus, bone, muscle, tonsil, kidney,
and sensitive at very early stages (up to 4 weeks) of therapy. mediastinum, pleura, and paranasal sinuses. The prognosis of
Many clinical studies of patients enrolled on ALL treatment relapse depends on the time from diagnosis (earlier is worse),
protocols have revealed strikingly similar results. Fast clearance leukocyte count, immunophenotype, and genotype (similar to
Clinical remission
Diagnosis Week 6 Week 20
10 4 10 4 10 4
10 3 10 3 10 3
CD10 10 2 CD10 10 2 CD10 10 2
10 1 10 1 10 1
10 0 10 0 10 0
10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4
CD38 CD38 CD38
10 4 10 4 10 4
10 3 10 3 10 3
CD10 10 2 CD10 10 2 CD10 10 2
10 1 10 1 10 1
10 0 10 0 10 0
10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4
CD38 CD38 CD38
Fig 78.4 Different Kinetics of Leukemia Cytoreduction Revealed by Minimal Residual
Disease (MRD) Studies With Flow Cytometry. The left panels illustrate the leukemia-specific
immunophenotype (CD10 , CD38 ) determined at diagnosis in two children with ALL. This
+
−
phenotype is not found in normal bone marrow. Bone marrow samples were collected during
clinical remission from both patients. In one patient (top panels), 0.04% of mononuclear cells
expressed the leukemia-specific phenotype at week 6. MRD was undetectable by week 20. In
the other patient (bottom panels), a profound remission (MRD <0.01%) was achieved by week
6 and maintained at week 20.