Page 1254 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1254
CHaPter 90 Vaccines 1215
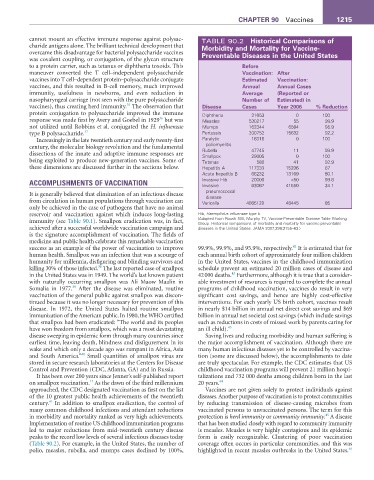
cannot mount an effective immune response against polysac- TABLE 90.2 Historical Comparisons of
charide antigens alone. The brilliant technical development that Morbidity and Mortality for Vaccine-
overcame this disadvantage for bacterial polysaccharide vaccines Preventable Diseases in the United States
was covalent coupling, or conjugation, of the glycan structure
to a protein carrier, such as tetanus or diphtheria toxoids. This Before
maneuver converted the T cell–independent polysaccharide Vaccination: after
vaccines into T cell–dependent protein–polysaccharide conjugate estimated Vaccination:
vaccines, and this resulted in B-cell memory, much improved annual annual Cases
immunity, usefulness in newborns, and even reduction in average (reported or
nasopharyngeal carriage (not seen with the pure polysaccharide number of estimated) in
35
vaccines), thus creating herd immunity. The observation that Disease Cases Year 2006 % reduction
protein conjugation to polysaccharide improved the immune Diphtheria 21053 0 100
36
response was made first by Avery and Goebel in 1929 but was Measles 530217 55 99.9
not utilized until Robbins et al. conjugated the H. influenzae Mumps 162344 6584 95.9
type B polysaccharide. 37 Pertussis 200752 15632 92.2
Increasingly in the late twentieth century and early twenty-first Paralytic 16316 0 100
century, the molecular biology revolution and the fundamental poliomyelitis
99.9
dissections of the innate and adaptive immune responses are Rubella 47745 11 100
29005
Smallpox
0
being exploited to produce new-generation vaccines. Some of Tetanus 580 41 92.9
these dimensions are discussed further in the sections below. Hepatitis A 117333 15296 87
Acute hepatitis B 66232 13169 80.1
<50
ACCOMPLISHMENTS OF VACCINATION Invasive Hib 20000 41550 99.8
34.1
63067
Invasive
pneumococcal
It is generally believed that elimination of an infectious disease disease
from circulation in human populations through vaccination can Varicella 4085120 48445 85
only be achieved in the case of pathogens that have no animal
reservoir and vaccination against which induces long-lasting Hib, Haemplhilus influenzae type b.
immunity (see Table 90.1). Smallpox eradication was, in fact, (Adapted from Roush SW, Murphy TV, Vaccine-Preventable Disease Table Working
Group. Historical comparisons of morbidity and mortality for vaccine-preventable
achieved after a successful worldwide vaccination campaign and diseases in the United States. JAMA 2007;298:2155–63.)
is the signature accomplishment of vaccination. The fields of
medicine and public health celebrate this remarkable vaccination
42
success as an example of the power of vaccination to improve 99.9%, 99.9%, and 95.9%, respectively. It is estimated that for
human health. Smallpox was an infection that was a scourge of each annual birth cohort of approximately four million children
humanity for millennia, disfiguring and blinding survivors and in the United States, vaccines in the childhood immunization
38
killing 30% of those infected. The last reported case of smallpox schedule prevent an estimated 20 million cases of disease and
43
in the United States was in 1949. The world’s last known patient 42 000 deaths. Furthermore, although it is true that a consider-
with naturally occurring smallpox was Ali Maow Maalin in able investment of resources is required to complete the annual
39
Somalia in 1977. After the disease was eliminated, routine programs of childhood vaccination, vaccines do result in very
vaccination of the general public against smallpox was discon- significant cost savings, and hence are highly cost-effective
tinued because it was no longer necessary for prevention of this interventions. For each yearly US birth cohort, vaccines result
disease. In 1972, the United States halted routine smallpox in nearly $14 billion in annual net direct cost savings and $69
immunization of the American public. In 1980, the WHO certified billion in annual net societal cost savings (which include savings
that smallpox had been eradicated: “The world and its peoples such as reductions in costs of missed work by parents caring for
have won freedom from smallpox, which was a most devastating an ill child). 43
disease sweeping in epidemic form through many countries since Saving lives and reducing morbidity and human suffering is
earliest time, leaving death, blindness and disfigurement in its the major accomplishment of vaccination. Although there are
wake and which only a decade ago was rampant in Africa, Asia many human infectious diseases yet to be controlled by vaccina-
40
and South America.” Small quantities of smallpox virus are tion (some are discussed below), the accomplishments to date
stored in secure research laboratories at the Centers for Disease are truly spectacular. For example, the CDC estimates that US
Control and Prevention (CDC, Atlanta, GA) and in Russia. childhood vaccination programs will prevent 21 million hospi-
It has been over 200 years since Jenner’s self-published report talizations and 732 000 deaths among children born in the last
17
on smallpox vaccination. As the dawn of the third millennium 20 years. 44
approached, the CDC designated vaccination as first on the list Vaccines are not given solely to protect individuals against
of the 10 greatest public health achievements of the twentieth diseases. Another purpose of vaccination is to protect communities
41
century. In addition to smallpox eradication, the control of by reducing transmission of disease-causing microbes from
many common childhood infections and attendant reductions vaccinated persons to unvaccinated persons. The term for this
45
in morbidity and mortality ranked as very high achievements. protection is herd immunity or community immunity. A disease
Implementation of routine US childhood immunization programs that has been studied closely with regard to community immunity
led to major reductions from mid-twentieth century disease is measles. Measles is very highly contagious and its epidemic
peaks to the record low levels of several infectious diseases today form is easily recognizable. Clustering of poor vaccination
(Table 90.2). For example, in the United States, the number of coverage often occurs in particular communities, and this was
46
polio, measles, rubella, and mumps cases declined by 100%, highlighted in recent measles outbreaks in the United States.