Page 257 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 257
238 PArT TwO Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
KEY CONCEPTS Th1 inflammation Th2 inflammation
CD4 Effector Phenotypes Antigen
presentation B
Th1 IFNγ IL-4 T IL-4 Plasma cell
• Produce interferon (IFN)-γ, interleukin (IL)-2, tumor necrosis factor h2 IgE
(TNF)-α and TNF-β (LT-α) T h1
• Stimulate Immunoglobulin (Ig)G2 and IgG3 class switching TNFα IL-5
• Responses mediated by macrophage activity APC
• Promotes phagocytic activity through: Blood
• FcγRIII cross-linking vessel Mast cell
• Complement deposition
• Opsonization APC/macrophage
• IFN-γ-mediated macrophage activation activation and Antigen
phagocytosis presentation Eosinophil
IL-6
Th2 IL-17? IL-17
• Produce IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, and IL-10 T TNFα
• Stimulate IgG4 and IgE class switching h17
• Responses mediated by mast cells and eosinophils APC APC Neutrophil
• Increases degranulation through:
• FcεRI cross-linking
• IL-5–mediated eosinophil activation Th17 inflammation
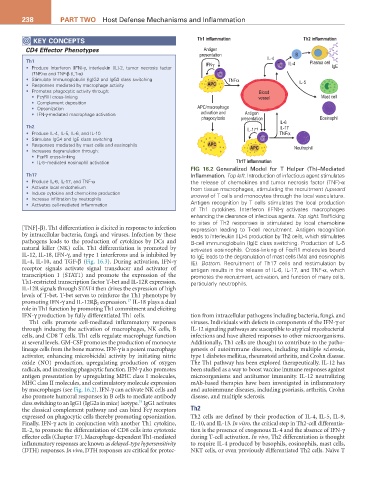
FIG 16.2 Generalized Model for T Helper (Th)–Mediated
Th17 Inflammation. Top left. Introduction of infectious agent stimulates
• Produce IL-6, IL-17, and TNF-α the release of chemokines and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α
• Activate local endothelium from tissue macrophages, stimulating the recruitment (upward
• Induce cytokine and chemokine production arrows) of T cells and monocytes through the local vasculature.
• Increase infiltration by neutrophils Antigen recognition by T cells stimulates the local production
• Activates cell-mediated inflammation
of Th1 cytokines. Interferon (IFN)-γ activates macrophages
enhancing the clearance of infectious agents. Top right. Trafficking
to sites of Th2 responses is stimulated by local chemokine
[TNF]-β). Th1 differentiation is elicited in response to infection expression leading to T-cell recruitment. Antigen recognition
by intracellular bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Infection by these leads to interleukin (IL)-4 production by Th2 cells, which stimulates
pathogens leads to the production of cytokines by DCs and B-cell immunoglobulin (Ig)E class switching. Production of IL-5
natural killer (NK) cells. Th1 differentiation is promoted by activates eosinophils. Cross-linking of FcεR1 molecules bound
IL-12, IL-18, IFN-γ, and type 1 interferons and is inhibited by to IgE leads to the degranulation of mast cells (Ma) and eosinophils
IL-4, IL-10, and TGF-β (Fig. 16.3). During activation, IFN-γ (E). Bottom. Recruitment of Th17 cells and restimulation by
receptor signals activate signal transducer and activator of antigen results in the release of IL-6, IL-17, and TNF-α, which
transcription 1 (STAT1) and promote the expression of the promotes the recruitment, activation, and function of many cells,
Th1-restricted transcription factor T-bet and IL-12R expression. particularly neutrophils.
IL-12R signals through STAT4 then drives the expression of high
levels of T-bet. T-bet serves to reinforce the Th1 phenotype by
17
promoting IFN-γ and IL-12Rβ 2 expression. IL-18 plays a dual
role in Th1 function by promoting Th1 commitment and eliciting
IFN-γ production by fully differentiated Th1 cells. tion from intracellular pathogens including bacteria, fungi, and
Th1 cells promote cell-mediated inflammatory responses viruses. Individuals with defects in components of the IFN-γ or
through inducing the activation of macrophages, NK cells, B IL-12 signaling pathways are susceptible to atypical mycobacterial
cells, and CD8 T cells. Th1 cells regulate macrophage function infections and have altered responses to other microorganisms.
at several levels. GM-CSF promotes the production of monocyte Additionally, Th1 cells are thought to contribute to the patho-
lineage cells from the bone marrow. IFN-γ is a potent macrophage genesis of autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis,
activator, enhancing microbicidal activity by initiating nitric type 1 diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn disease.
oxide (NO) production, upregulating production of oxygen The Th1 pathway has been explored therapeutically. IL-12 has
radicals, and increasing phagocytic function. IFN-γ also promotes been studied as a way to boost vaccine immune responses against
antigen presentation by upregulating MHC class I molecules, microorganisms and antitumor immunity. IL-12 neutralizing
MHC class II molecules, and costimulatory molecule expression mAb-based therapies have been investigated in inflammatory
by macrophages (see Fig. 16.2). IFN-γ can activate NK cells and and autoimmune diseases, including psoriasis, arthritis, Crohn
also promote humoral responses in B cells to mediate antibody disease, and multiple sclerosis.
18
class switching to an IgG1 (IgG2a in mice) isotype. IgG1 activates
the classical complement pathway and can bind Fcγ receptors Th2
expressed on phagocytic cells thereby promoting opsonization. Th2 cells are defined by their production of IL-4, IL-5, IL-9,
Finally, IFN-γ acts in conjunction with another Th1 cytokine, IL-10, and IL-13. In vitro, the critical step in Th2-cell differentia-
IL-2, to promote the differentiation of CD8 cells into cytotoxic tion is the presence of exogenous IL-4 and the absence of IFN-γ
effector cells (Chapter 17). Macrophage-dependent Th1-mediated during T-cell activation. In vivo, Th2 differentiation is thought
inflammatory responses are known as delayed-type hypersensitivity to require IL-4 produced by basophils, eosinophils, mast cells,
(DTH) responses. In vivo, DTH responses are critical for protec- NKT cells, or even previously differentiated Th2 cells. Naïve T