Page 259 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 259
240 PArT TwO Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
TABLE 16.2 T-Cell Effector responses to Th1 NK
Selected Pathogens
IFNγ
Organism Nature of the Immune response TLR
DC Stat 1, 4
Bacteria Tcell Tbet Th1
Borrelia burgdorferi T-helper (Th1) responses associated IL-4 Hlx
with protection and joint pathology IL-12, IL-18
Chlamydia trachomatis Th1 responses protective and source A IL-23, IL-27 Th2
of pathology
Helicobacter pylori Th1 responses involved in ulcer
formation
Legionella pneumophila Th1 responses associated with
immunity Th2 Mast cell
Listeria monocytogenes Th1 responses are protective:
interferon (IFN)-γ from γδ T cells and IL-4
CD8 T cells is important DC
Stat 6
Mycobacterium leprae Severity and phenotype of disease GATA 3 Th2
depends on Th1 and Th2 ? IFNγ
predominance Naive
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Th1 responses control infection B Cell Th1
Treponema pallidum Th1 resolves infection; Th2 chronic
Yersinia pestis Th1 and Th17 responses associated
with immunity
Fungi TGFβ
IL-6
Aspergillus fumigatus Th2 production predominates; does DC
Th1 offer protection? RORγt Th17
Blastomyces dermatitidis Th1 protects; Th2 switch in progressive IL-23 Naive IFNγ IL-4
disease C Cell Th1 Th2
Candida albicans Th17 responses are protective
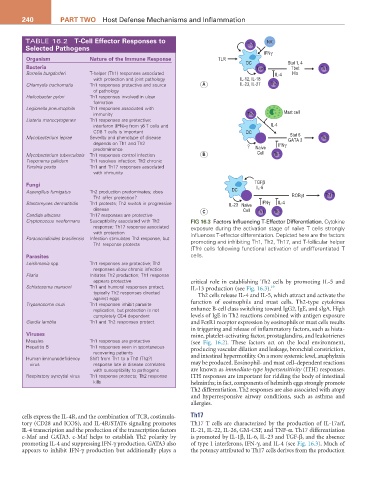
Cryptococcus neoformans Susceptibility associated with Th2 FIG 16.3 Factors Influencing T-Effector Differentiation. Cytokine
response; Th17 response associated exposure during the activation stage of naïve T cells strongly
with protection influences T-effector differentiation. Depicted here are the factors
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Infection stimulates Th2 response, but promoting and inhibiting Th1, Th2, Th17, and T-follicular helper
Th1 response protects
(Tfh) cells following functional activation of undifferentiated T
Parasites cells.
Leishmania spp. Th1 responses are protective; Th2
responses allow chronic infection
Filaria Initiates Th2 production; Th1 response
appears protective critical role in establishing Th2 cells by promoting IL-5 and
Schistosoma mansoni Th1 and humoral responses protect; IL-13 production (see Fig. 16.3). 19
typically Th2 responses directed Th2 cells release IL-4 and IL-5, which attract and activate the
against eggs
Trypanosoma cruzi Th1 responses inhibit parasite function of eosinophils and mast cells. Th2-type cytokines
replication, but protection is not enhance B-cell class switching toward IgG2, IgE, and sIgA. High
completely CD4 dependent levels of IgE in Th2 reactions combined with antigen exposure
Giardia lamblia Th1 and Th2 responses protect and FcεR1 receptor expression by eosinophils or mast cells results
in triggering and release of inflammatory factors, such as hista-
Viruses mine, platelet-activating factor, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes
Measles Th1 responses are protective (see Fig. 16.2). These factors act on the local environment,
Hepatitis B Th1 responses seen in spontaneous producing vascular dilation and leakage, bronchial constriction,
recovering patients
Human immunodeficiency Shift from Th1 to a Th0 (Th2?) and intestinal hypermotility. On a more systemic level, anaphylaxis
virus response late in disease correlates may be produced. Eosinophil- and mast cell–dependent reactions
with susceptibility to pathogens are known as immediate-type hypersensitivity (ITH) responses.
Respiratory syncytial virus Th1 response protects; Th2 response ITH responses are important for ridding the body of intestinal
kills helminths; in fact, components of helminth eggs strongly promote
Th2 differentiation. Th2 responses are also associated with atopy
and hyperresponsive airway conditions, such as asthma and
allergies.
cells express the IL-4R, and the combination of TCR, costimula- Th17
tory (CD28 and ICOS), and IL-4R/STAT6 signaling promotes Th17 T cells are characterized by the production of IL-17a/f,
IL-4 transcription and the production of the transcription factors IL-21, IL-22, IL-26, GM-CSF, and TNF-α. Th17 differentiation
c-Maf and GATA3. c-Maf helps to establish Th2 polarity by is promoted by IL-1β, IL-6, IL-23 and TGF-β, and the absence
promoting IL-4 and suppressing IFN-γ production. GATA3 also of type 1 interferons, IFN-γ, and IL-4 (see Fig. 16.3). Much of
appears to inhibit IFN-γ production but additionally plays a the potency attributed to Th17 cells derives from the production