Page 271 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 271
252 PART TwO Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
Primary infection TABLE 17.2 Human and Mouse Natural
10 4
1.2% Killer (NK) Cell Receptors (Partial List)
10 3 Species Ligands
(H, Human;
(H, Human; M,
NP tetramer 10 2 Receptor M, Mouse) Function Mouse)
H, M
Inhibitory
LILRB1
HLA-class I
10 1 NP tetramer + KIR2DL1, 2, 3 H Inhibitory HLA-C
H
KIR2DL4
HLA-G
Activating
KIR2DL5 H Inhibitory ?
CD62L
10 0 KIR3DL1 H Inhibitory HLA-Bw4
10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 KIR3DL2 H Inhibitory HLA-A3, A11
KIR3DL3 H Inhibitory ?
Secondary infection
10 4 KIR2DS1, 2, H Activating HLA-class I
23.7% 3, 4, 5
KIR3DS1 H Activating HLA-Bw4
10 3 CD94/NKG2A H, M Inhibitory H; HLA-E
M; Qa-1b
NP tetramer 10 2 CD94/NKG2C, H, M Activating H; HLA-E,
M; Qa-1b
E
M; H60, MULT1,
10 1 NP tetramer – NKG2D H, M Activating H; MICA/B, ULBP1–4,
CD62L RAE1
CD16 (FcγRIII) H, M Activating Immune complexes
10 0 CD27 H, M Activating CD70
10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4
CD244 (2B4) H, M Activating/ CD48
Inhibitory
10 4 Ly49A-C, E-G, M Inhibitory MHC-class I
I-O
Ly49D M Activating H-2D d
10 3 Ly49H M Activating MCMV m157
k
Ly49P M Activating H-2D /MCMV m04
IFNγ 10 2 KLRG1 H, M Inhibitory E-, R-, N-cadherins
Inhibitory
NKR-P1A
H
LLT1 (CLEC2D)
NKR-P1A, B, M Activating/ Clr family
10 1 C, E, F Inhibitory
NKR-P1B, D M Inhibitory Clr-b, Clr-g
PILRα/PILRβ M Activating/ O-glycosylated CD99
10 0
10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 Inhibitory
CD8 NKp46 H, M Activating Viral hemagglutinin,
HSPG
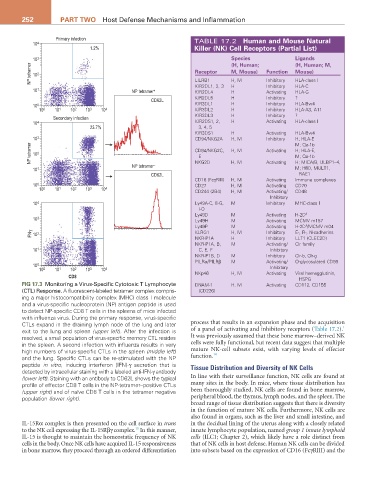
FIG 17.3 Monitoring a Virus-Specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte DNAM-1 H, M Activating CD112, CD155
(CTL) Response. A fluorescent-labeled tetramer complex compris- (CD226)
ing a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecule
and a virus-specific nucleoprotein (NP) antigen peptide is used
to detect NP-specific CD8 T cells in the spleens of mice infected
with influenza virus. During the primary response, virus-specific
CTLs expand in the draining lymph node of the lung and later process that results in an expansion phase and the acquisition
1
exit to the lung and spleen (upper left). After the infection is of a panel of activating and inhibitory receptors (Table 17.2).
resolved, a small population of virus-specific memory CTL resides It was previously assumed that these bone marrow–derived NK
in the spleen. A second infection with influenza results in very cells were fully functional, but recent data suggest that multiple
high numbers of virus-specific CTLs in the spleen (middle left) mature NK-cell subsets exist, with varying levels of effector
14
and the lung. Specific CTLs can be re-stimulated with the NP function.
peptide in vitro, inducing interferon (IFN)-γ secretion that is Tissue Distribution and Diversity of NK Cells
detected by intracellular staining with a labeled anti-IFN-γ antibody
(lower left). Staining with an antibody to CD62L shows the typical In line with their surveillance function, NK cells are found at
profile of effector CD8 T cells in the NP-tetramer–positive CTLs many sites in the body. In mice, where tissue distribution has
(upper right) and of naïve CD8 T cells in the tetramer negative been thoroughly studied, NK cells are found in bone marrow,
population (lower right). peripheral blood, the thymus, lymph nodes, and the spleen. The
broad range of tissue distribution suggests that there is diversity
in the function of mature NK cells. Furthermore, NK cells are
also found in organs, such as the liver and small intestine, and
IL-15Rα complex is then presented on the cell surface in trans in the decidual lining of the uterus along with a closely related
15
to the NK cell expressing the IL-15Rβγ complex. In this manner, innate lymphocyte population, named group 1 innate lymphoid
IL-15 is thought to maintain the homeostatic frequency of NK cells (ILC1; Chapter 2), which likely have a role distinct from
cells in the body. Once NK cells have acquired IL-15 responsiveness that of NK cells in host defense. Human NK cells can be divided
in bone marrow, they proceed through an ordered differentiation into subsets based on the expression of CD16 (FcγRIII) and the