Page 322 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 322
302 Part two Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
C3 C3b(H 0) C6 C8 C9
2
SS SS C5b
C3 convertase C7
S S
S HS COOH S
S-C=O
C3a Poly C9
SS
S
S
S-C=O
C3b
SS S S SS S S
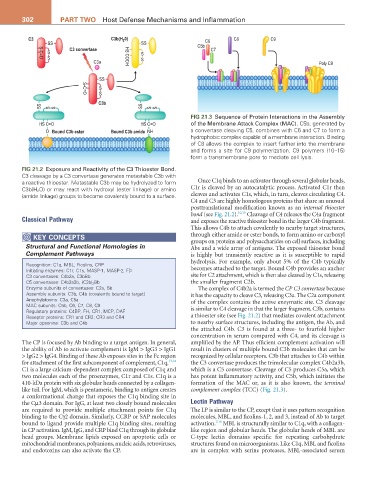
FIG 21.3 Sequence of Protein Interactions in the Assembly
HS C=O HS C=O of the Membrane Attack Complex (MAC). C5b, generated by
O Bound C3b ester Bound C3b amide NH a convertase cleaving C5, combines with C6 and C7 to form a
hydrophobic complex capable of a membrane interaction. Binding
of C8 allows the complex to insert further into the membrane
and forms a site for C9 polymerization. C9 polymers (10–15)
form a transmembrane pore to mediate cell lysis.
FIG 21.2 Exposure and Reactivity of the C3 Thioester Bond.
C3 cleavage by a C3 convertase generates metastable C3b with
a reactive thioester. Metastable C3b may be hydrolyzed to form Once C1q binds to an activator through several globular heads,
C3b(H 2 O) or may react with hydroxyl (ester linkage) or amino C1r is cleaved by an autocatalytic process. Activated C1r then
(amide linkage) groups to become covalently bound to a surface. cleaves and activates C1s, which, in turn, cleaves circulating C4.
C4 and C3 are highly homologous proteins that share an unusual
posttranslational modification known as an internal thioester
bond (see Fig. 21.2). 10,15 Cleavage of C4 releases the C4a fragment
Classical Pathway and exposes the reactive thioester bond in the larger C4b fragment.
This allows C4b to attach covalently to nearby target structures,
KEY CoNCEPtS through either amide or ester bonds, to form amino or carboxyl
Structural and Functional Homologies in groups on proteins and polysaccharides on cell surfaces, including
Abs and a wide array of antigens. The exposed thioester bond
Complement Pathways is highly but transiently reactive as it is susceptible to rapid
hydrolysis. For example, only about 5% of the C4b typically
Recognition: C1q, MBL, Ficolins, CRP
Initiating enzymes: C1r, C1s, MASP-1, MASP-2, FD becomes attached to the target. Bound C4b provides an anchor
C3 convertases: C4b2a, C3bBb site for C2 attachment, which is then also cleaved by C1s, releasing
C5 convertases: C4b2a3b, (C3b) 2 Bb the smaller fragment C2b.
Enzyme subunits of convertases: C2a, Bb The complex of C4b2a is termed the CP C3 convertase because
Assembly subunits: C3b, C4b (covalently bound to target) it has the capacity to cleave C3, releasing C3a. The C2a component
Anaphylatoxins: C3a, C5a of the complex contains the active enzymatic site. C3 cleavage
MAC subunits: C5b, C6, C7, C8, C9
Regulatory proteins: C4BP, FH, CR1, MCP, DAF is similar to C4 cleavage in that the larger fragment, C3b, contains
Receptor proteins: CR1 and CR2; CR3 and CR4 a thioester site (see Fig. 21.2) that mediates covalent attachment
Major opsonins: C3b and C4b to nearby surface structures, including the antigen, the Ab, and
the attached C4b. C3 is found at a three- to fourfold higher
concentration in serum compared with C4, and its cleavage is
The CP is focused by Ab binding to a target antigen. In general, amplified by the AP. Thus efficient complement activation will
the ability of Ab to activate complement is IgM > IgG3 > IgG1 result in clusters of multiple bound C3b molecules that can be
> IgG2 > IgG4. Binding of these Ab exposes sites in the Fc region recognized by cellular receptors. C3b that attaches to C4b within
for attachment of the first subcomponent of complement, C1q. 13,14 the C3 convertase produces the trimolecular complex C4b2a3b,
C1 is a large calcium-dependent complex composed of C1q and which is a C5 convertase. Cleavage of C5 produces C5a, which
two molecules each of the proenzymes, C1r and C1s. C1q is a has potent inflammatory activity, and C5b, which initiates the
410-kDa protein with six globular heads connected by a collagen- formation of the MAC or, as it is also known, the terminal
like tail. For IgM, which is pentameric, binding to antigen creates complement complex (TCC) (Fig. 21.3).
a conformational change that exposes the C1q binding site in
the Cµ3 domain. For IgG, at least two closely bound molecules Lectin Pathway
are required to provide multiple attachment points for C1q The LP is similar to the CP, except that it uses pattern recognition
binding to the Cγ2 domain. Similarly, CCRP or SAP molecules molecules, MBL, and ficolins-1, 2, and 3, instead of Ab to target
7,16
bound to ligand provide multiple C1q binding sites, resulting activation. MBL is structurally similar to C1q, with a collagen-
in CP activation. IgM, IgG, and CRP bind C1q through its globular like region and globular heads. The globular heads of MBL are
head groups. Membrane lipids exposed on apoptotic cells or C-type lectin domains specific for repeating carbohydrate
mitochondrial membranes, polyanions, nucleic acids, retroviruses, structures found on microorganisms. Like C1q, MBL and ficolins
and endotoxins can also activate the CP. are in complex with serine proteases, MBL-associated serum