Page 329 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 329
CHaPtEr 21 The Human Complement System: Basic Concepts and Clinical Relevance 309
COMPLEMENT DEFICIENCIES
CR3 Genetics and Incidence
IgM CR1
iC3b Complete genetic deficiencies of complement proteins are rare,
CRP with an estimated combined prevalence of 0.03% for any inherited
C3b FcγR complete deficiency (excluding MBL deficiency) in the general
C1q population. 2-4,56-58 For most components, inheritance is autosomal
and expression is codominant, so complete deficiency is homo-
MBL zygous recessive and heterozygotes express half levels. There are
C1qR two C4 genes (C4A and C4B), so a range of partial deficiencies
SAP can be observed. All cases of C1-INH deficiency have been
FcγR heterozygous, and P deficiency is X-linked. MBL is found in
multiple allelic forms with different levels of expression ranging
from 5 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL) to more than 5 micro-
grams per milliliter (µg/mL) in plasma. Deficiencies specific to
TGF-β, IL-10 the LP are not detected by the screening assays described below
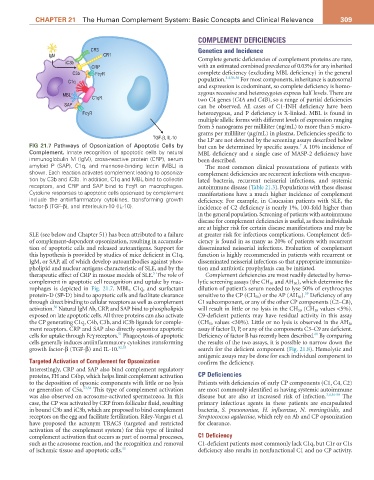
FIG 21.7 Pathways of Opsonization of Apoptotic Cells by but can be determined by specific assays. A 10% incidence of
7
Complement. Innate recognition of apoptotic cells by natural MBL deficiency and a single case of MASP-2 deficiency have
immunoglobulin M (IgM), cross-reactive protein (CRP), serum been described.
amyloid P (SAP), C1q, and mannose-binding lectin (MBL) is The most common clinical presentations of patients with
shown. Each reaction activates complement leading to opsoniza- complement deficiencies are recurrent infections with encapsu-
tion by C3b and iC3b. In addition, C1q and MBL bind to collectin lated bacteria, recurrent neisserial infections, and systemic
receptors, and CRP and SAP bind to FcγR on macrophages. autoimmune disease (Table 21.3). Populations with these disease
Cytokine responses to apoptotic cells opsonized by complement manifestations have a much higher incidence of complement
include the antiinflammatory cytokines, transforming growth deficiency. For example, in Caucasian patients with SLE, the
factor-β (TGF-β), and interleukin-10 (IL-10). incidence of C2 deficiency is nearly 1%, 100-fold higher than
in the general population. Screening of patients with autoimmune
disease for complement deficiencies is useful, as these individuals
are at higher risk for certain disease manifestations and may be
SLE (see below and Chapter 51) has been attributed to a failure at greater risk for infectious complications. Complement defi-
of complement-dependent opsonization, resulting in accumula- ciency is found in as many as 20% of patients with recurrent
tion of apoptotic cells and released autoantigens. Support for disseminated neisserial infections. Evaluation of complement
this hypothesis is provided by studies of mice deficient in C1q, function is highly recommended in patients with recurrent or
IgM, or SAP, all of which develop autoantibodies against phos- disseminated neisserial infections so that appropriate immuniza-
pholipid and nuclear antigens characteristic of SLE, and by the tion and antibiotic prophylaxis can be initiated.
5
therapeutic effect of CRP in mouse models of SLE. The role of Complement deficiencies are most readily detected by hemo-
complement in apoptotic cell recognition and uptake by mac- lytic screening assays (the CH 50 and AH 50 ), which determine the
rophages is depicted in Fig. 21.7. MBL, C1q, and surfactant dilution of patient’s serum needed to lyse 50% of erythrocytes
59
protein-D (SP-D) bind to apoptotic cells and facilitate clearance sensitive to the CP (CH 50 ) or the AP (AH 50 ). Deficiency of any
through direct binding to cellular receptors as well as complement C1 subcomponent, or any of the other CP components (C2–C8),
50
activation. Natural IgM Ab, CRP, and SAP bind to phospholipids will result in little or no lysis in the CH 50 (CH 50 values <5%).
exposed on late apoptotic cells. All three proteins can also activate C9-deficient patients may have residual activity in this assay
the CP generating C1q, C4b, C3b, and iC3b ligands for comple- (CH 50 values <30%). Little or no lysis is observed in the AH 50
ment receptors. CRP and SAP also directly opsonize apoptotic assay if factor D, P, or any of the components C3–C9 are deficient.
60
51
cells for uptake through Fcγ receptors. Phagocytosis of apoptotic Deficiency of factor B has recently been described. By comparing
cells generally induces antiinflammatory cytokines transforming the results of the two assays, it is possible to narrow down the
growth factor-β (TGF-β) and IL-10. 52,53 search for the deficient component (Fig. 21.8). Hemolytic and
antigenic assays may be done for each individual component to
Targeted Activation of Complement for Opsonization confirm the deficiency.
Interestingly, CRP and SAP also bind complement regulatory
proteins, FH and C4bp, which helps limit complement activation CP Deficiencies
to the deposition of opsonic components with little or no lysis Patients with deficiencies of early CP components (C1, C4, C2)
or generation of C5a. 53,54 This type of complement activation are most commonly identified as having systemic autoimmune
was also observed on acrosome-activated spermatozoa. In this disease but are also at increased risk of infection. 3,4,56-58 The
case, the CP was activated by CRP from follicular fluid, resulting primary infectious agents in these patients are encapsulated
in bound C3b and iC3b, which are proposed to bind complement bacteria, S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, N. meningitidis, and
receptors on the egg and facilitate fertilization. Riley-Vargas et al. Streptococcus agalactiae, which rely on Ab and CP opsonization
have proposed the acronym TRACS (targeted and restricted for clearance.
activation of the complement system) for this type of limited
complement activation that occurs as part of normal processes, C1 Deficiency
such as the acrosome reaction, and the recognition and removal C1-deficient patients most commonly lack C1q, but C1r or C1s
of ischemic tissue and apoptotic cells. 55 deficiency also results in nonfunctional C1 and no CP activity.