Page 34 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 34
20 Part one Principles of Immune Response
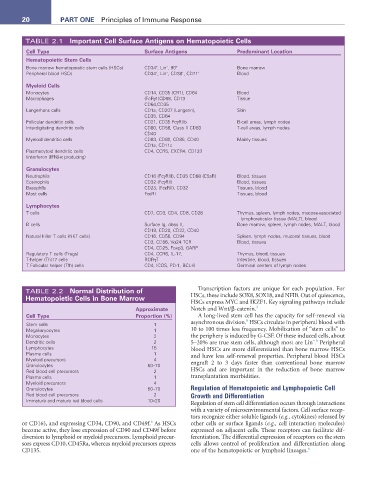
TABLE 2.1 Important Cell Surface antigens on Hematopoietic Cells
Cell type Surface antigens Predominant Location
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
+
−
Bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) CD34 , Lin , 90 + Bone marrow
+
Peripheral blood HSCs CD34 , Lin , CD38 , CD71 + Blood
−
+
Myeloid Cells
Monocytes CD14, CD35 (CR1), CD64 Blood
Macrophages (FcRγ1)CD68, CD13 Tissue
CD64,CD35
Langerhans cells CD1a, CD207 (Langerin), Skin
CD35, CD64
Follicular dendritic cells CD21, CD35 FcγRIIb B-cell areas, lymph nodes
Interdigitating dendritic cells CD80, CD56, Class II CD83 T-cell areas, lymph nodes
CD40
Myeloid dendritic cells CD83, CD80, CD86, CD40 Mainly tissues
CD1a, CD11c
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells CD4, CCR5, CXCR4, CD123
(interferon [IFN]-α producing)
Granulocytes
Neutrophils CD16 (FcγRIII), CD35 CD88 (C5aR) Blood, tissues
Eosinophils CD32 (FcγRII) Blood, tissues
Basophils CD23, (FcεRII), CD32 Tissues, blood
Mast cells FcεRI Tissues, blood
Lymphocytes
T cells CD7, CD3, CD4, CD8, CD28 Thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, mucosa-associated
lymphoreticular tissue (MALT), blood
B cells Surface Ig, class II, Bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes, MALT, blood
CD19, CD20, CD22, CD40
Natural killer T cells (NKT cells) CD16, CD56, CD94 Spleen, lymph nodes, mucosal tissues, blood
CD3, CD56, Vα24 TCR Blood, tissues
CD4, CD25, Foxp3, GARP
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) CD4, CCR6, IL-17, Thymus, blood, tissues
T-helper (Th)17 cells RORγT Intestine, blood, tissues
T Follicular helper (Tfh) cells CD4, ICOS, PD-1, BCL-6 Germinal centers of lymph nodes
TABLE 2.2 normal Distribution of Transcription factors are unique for each population. For
Hematopoietic Cells in Bone Marrow HSCs, these include SOX8, SOX18, and NFIB. Out of quiescence,
HSCs express MYC and IKZF1. Key signaling pathways include
approximate Notch and Wnt/β-catenin. 3
Cell type Proportion (%) A long-lived stem cell has the capacity for self-renewal via
9
Stem cells 1 asynchronous division. HSCs circulate in peripheral blood with
Megakaryocytes 1 10 to 100 times less frequency. Mobilization of “stem cells” to
Monocytes 2 the periphery is induced by G-CSF. Of these induced cells, about
Dendritic cells 2 5–20% are true stem cells, although most are Lin . Peripheral
− 9
Lymphocytes 15 blood HSCs are more differentiated than bone marrow HSCs
Plasma cells 1 and have less self-renewal properties. Peripheral blood HSCs
Myeloid precursors 4 engraft 2 to 3 days faster than conventional bone marrow
Granulocytes 50–70
Red blood cell precursors 2 HSCs and are important in the reduction of bone marrow
Plasma cells 1 transplantation morbidities.
Myeloid precursors 4
Granulocytes 50–70 Regulation of Hematopoietic and Lymphopoietic Cell
Red blood cell precursors 2 Growth and Differentiation
Immature and mature red blood cells 10–20
Regulation of stem cell differentiation occurs through interactions
with a variety of microenvironmental factors. Cell surface recep-
tors recognize either soluble ligands (e.g., cytokines) released by
6
or CD16), and expressing CD34, CD90, and CD49f. As HSCs other cells or surface ligands (e.g., cell interaction molecules)
become active, they lose expression of CD90 and CD49f before expressed on adjacent cells. These receptors can facilitate dif-
diversion to lymphoid or myeloid precursors. Lymphoid precur- ferentiation. The differential expression of receptors on the stem
sors express CD10, CD45Ra, whereas myeloid precursors express cells allows control of proliferation and differentiation along
CD135. one of the hematopoietic or lymphoid lineages. 6