Page 346 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 346
326 Part two Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
superoxide production were those with missense or splice muta-
tions in the first 309 amino acids of gp91 phox . Those with missense
mutations involving amino acids 310–587 had no residual
superoxide production, regardless of protein levels. Therefore
identification of the specific molecular subtype of CGD and
specific mutation has important implications for severity and
survival. Interestingly, mortality curves did not diverge until
after age 20 years, suggesting that residual superoxide production
determines later toxicities, such as liver dysfunction, not early
childhood mortality from infection. It is critical to keep in mind
that this comprehensive study included data from patients fol-
lowed for up to 30 years—that is, a significant number of patients
were born before the advent of modern antimicrobials. Therefore
survival of a child born in the current age and who receives ideal
management may well exceed that in the reported population.
CLINICaL PEarLS
Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD)
• CGD comprises a group of five inherited disorders with a common
phenotype.
• Infections with catalase-positive bacteria and fungi and granuloma
formation in the gastrointestinal and urinary tract are major problems
in CGD.
• Oral prophylactic antibiotics and subcutaneous interferon (IFN)-γ
injections three times a week are currently recommended for CGD.
• Diagnosis can be made via nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) test or dihy-
drorhodamine (DHR) assay, the latter being a more sensitive diagnostic
tool.
• Bone marrow transplantation is highly effective and curative.
Diagnosis of CGD
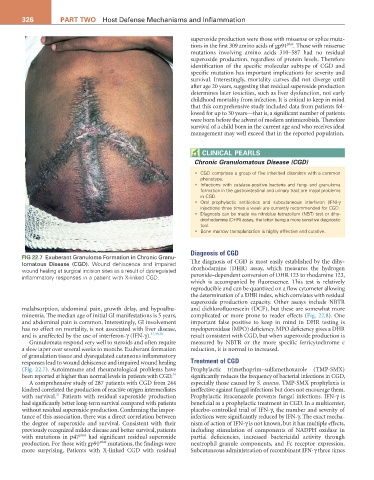
FIG 22.7 Exuberant Granuloma Formation in Chronic Granu-
lomatous Disease (CGD). Wound dehiscence and impaired The diagnosis of CGD is most easily established by the dihy-
wound healing at surgical incision sites as a result of dysregulated drorhodamine (DHR) assay, which measures the hydrogen
inflammatory responses in a patient with X-linked CGD. peroxide–dependent conversion of DHR 123 to rhodamine 123,
which is accompanied by fluorescence. This test is relatively
reproducible and can be quantized on a flow cytometer allowing
the determination of a DHR index, which correlates with residual
superoxide production capacity. Other assays include NBTR
malabsorption, abdominal pain, growth delay, and hypoalbu- and dichlorofluorescein (DCF), but these are somewhat more
minemia. The median age of initial GI manifestations is 5 years, complicated or more prone to reader effects (Fig. 22.8). One
and abdominal pain is common. Interestingly, GI involvement important false positive to keep in mind in DHR testing is
has no effect on mortality, is not associated with liver disease, myeloperoxidase (MPO) deficiency. MPO deficiency gives a DHR
and is unaffected by the use of interferon-γ (IFN-γ). 31,33,38 result consistent with CGD, but when superoxide production is
Granulomata respond very well to steroids and often require measured by NBTR or the more specific ferricytochrome c
a slow taper over several weeks to months. Exuberant formation reduction, it is normal to increased.
of granulation tissue and dysregulated cutaneous inflammatory
responses lead to wound dehiscence and impaired wound healing Treatment of CGD
(Fig. 22.7). Autoimmune and rheumatological problems have Prophylactic trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX)
been reported at higher than normal levels in patients with CGD. 39 significantly reduces the frequency of bacterial infections in CGD,
A comprehensive study of 287 patients with CGD from 244 especially those caused by S. aureus. TMP-SMX prophylaxis is
kindred correlated the production of reactive oxygen intermediates ineffective against fungal infections but does not encourage them.
31
with survival. Patients with residual superoxide production Prophylactic itraconazole prevents fungal infections. IFN-γ is
had significantly better long-term survival compared with patients beneficial as a prophylactic treatment in CGD. In a multicenter,
without residual superoxide production. Confirming the impor- placebo-controlled trial of IFN-γ, the number and severity of
tance of this association, there was a direct correlation between infections were significantly reduced by IFN-γ. The exact mecha-
the degree of superoxide and survival. Consistent with their nism of action of IFN-γ is not known, but it has multiple effects,
previously recognized milder disease and better survival, patients including stimulation of components of NADPH oxidase in
with mutations in p47 phox had significant residual superoxide partial deficiencies, increased bactericidal activity through
production. For those with gp91 phox mutations, the findings were neutrophil granule components, and Fc receptor expression.
more surprising. Patients with X-linked CGD with residual Subcutaneous administration of recombinant IFN-γ three times