Page 347 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 347
CHaPtEr 22 Phagocyte Deficiencies 327
A B
C
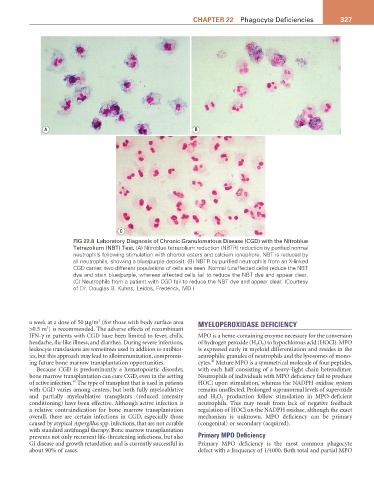
FIG 22.8 Laboratory Diagnosis of Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD) with the Nitroblue
Tetrazolium (NBT) Test. (A) Nitroblue tetrazolium reduction (NBTR) reduction by purified normal
neutrophils following stimulation with phorbol esters and calcium ionophore. NBT is reduced by
all neutrophils, showing a blue/purple deposit. (B) NBTR by purified neutrophils from an X-linked
CGD carrier; two different populations of cells are seen. Normal (unaffected cells) reduce the NBT
dye and stain blue/purple, whereas affected cells fail to reduce the NBT dye and appear clear.
(C) Neutrophils from a patient with CGD fail to reduce the NBT dye and appear clear. (Courtesy
of Dr. Douglas B. Kuhns, Leidos, Frederick, MD.)
2
a week at a dose of 50 µg/m (for those with body surface area MYELOPEROXIDASE DEFICIENCY
2
>0.5 m ) is recommended. The adverse effects of recombinant
IFN-γ in patients with CGD have been limited to fever, chills, MPO is a heme-containing enzyme necessary for the conversion
headache, flu-like illness, and diarrhea. During severe infections, of hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) to hypochlorous acid (HOCl). MPO
leukocyte transfusions are sometimes used in addition to antibiot- is expressed early in myeloid differentiation and resides in the
ics, but this approach may lead to alloimmunization, compromis- azurophilic granules of neutrophils and the lysosomes of mono-
41
ing future bone marrow transplantation opportunities. cytes. Mature MPO is a symmetrical molecule of four peptides,
Because CGD is predominantly a hematopoietic disorder, with each half consisting of a heavy–light chain heterodimer.
bone marrow transplantation can cure CGD, even in the setting Neutrophils of individuals with MPO deficiency fail to produce
40
of active infection. The type of transplant that is used in patients HOCl upon stimulation, whereas the NADPH oxidase system
with CGD varies among centers, but both fully myeloablative remains unaffected. Prolonged supranormal levels of superoxide
and partially myeloablative transplants (reduced intensity and H 2 O 2 production follow stimulation in MPO-deficient
conditioning) have been effective. Although active infection is neutrophils. This may result from lack of negative feedback
a relative contraindication for bone marrow transplantation regulation of HOCl on the NADPH oxidase, although the exact
overall, there are certain infections in CGD, especially those mechanism is unknown. MPO deficiency can be primary
caused by atypical Aspergillus spp. infections, that are not curable (congenital) or secondary (acquired).
with standard antifungal therapy. Bone marrow transplantation
prevents not only recurrent life-threatening infections, but also Primary MPO Deficiency
GI disease and growth retardation and is currently successful in Primary MPO deficiency is the most common phagocyte
about 90% of cases. defect with a frequency of 1/4000. Both total and partial MPO