Page 377 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 377
CHaPtEr 24 Eosinophils and Eosinophilia 357
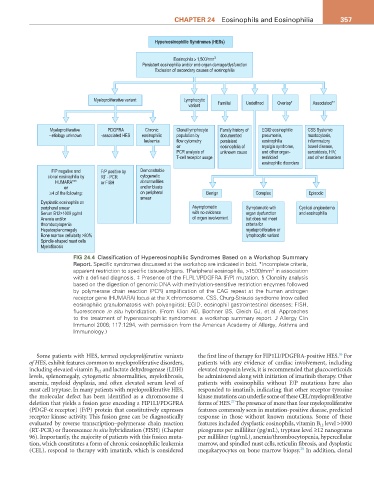
Hypereosinophilic Syndromes (HESs)
Eosinophils > 1,500/mm 3
Persistent eosinophilia and/or end-organ damage/dysfunction
Exclusion of secondary causes of eosinophilia
Myeloproliferative variant Lymphocytic
variant Familial Undefined Overlap* Associated**
Myeloproliferative PDGFRA Chronic Clonal lymphocyte Family history of EGID eosinophilic CSS Systemic
- etiology unknown -associated HES eosinophilic population by documented pneumonia, mastocytosis,
leukemia flow cytometry persistent eosinophilia inflammatory
or eosinophilia of myalgia syndrome, bowel disease,
PCR analysis of unknown cause and other organ- sarcoidosis, HIV,
T-cell receptor usage restricted and other disorders
eosinophilic disorders
F/P negative and F/P positive by Demonstrable
clonal eosinophilia by RT - PCR cytogenetic
HUMARA*** or FISH abnormalities
or and/or blasts
≥4 of the following: on peripheral Benign Complex Episodic
smear
Dysplastic eosinophils on
peripheral smear Asymptomatic Symptomatic with Cyclical angioedema
Serum B12>1000 pg/ml with no evidence organ dysfunction and eosinophilia
Anemia and/or of organ involvement but does not meet
thrombocytopenia criteria for
Hepatosplenomegaly myeloproliferative or
Bone marrow cellularity >80% lymphocytic variant
Spindle-shaped mast cells
Myelofibrosis
FIG 24.4 Classification of Hypereosinophilic Syndromes Based on a Workshop Summary
Report. Specific syndromes discussed at the workshop are indicated in bold. *Incomplete criteria,
apparent restriction to specific tissues/organs. †Peripheral eosinophilia, >1500/mm in association
3
with a defined diagnosis. ‡ Presence of the FLPL1/PDGFRA (F/P) mutation. § Clonality analysis
based on the digestion of genomic DNA with methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes followed
by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of the CAG repeat at the human androgen
receptor gene (HUMARA) locus at the X chromosome. CSS, Churg-Strauss syndrome (now called
eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis); EGID, eosinophil gastrointestinal diseases; FISH,
fluorescence in situ hybridization. (From Klion AD, Bochner BS, Gleich GJ, et al. Approaches
to the treatment of hypereosinophilic syndromes: a workshop summary report. J Allergy Clin
Immunol 2006; 117:1294, with permission from the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and
Immunology.)
26
Some patients with HES, termed myeloproliferative variants the first line of therapy for FIP1LI/PDGFRA-positive HES. For
of HES, exhibit features common to myeloproliferative disorders, patients with any evidence of cardiac involvement, including
including elevated vitamin B 12 and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) elevated troponin levels, it is recommended that glucocorticoids
levels, splenomegaly, cytogenetic abnormalities, myelofibrosis, be administered along with initiation of imatinib therapy. Other
anemia, myeloid dysplasia, and often elevated serum level of patients with eosinophilia without F/P mutations have also
mast cell tryptase. In many patients with myeloproliferative HES, responded to imatinib, indicating that other receptor tyrosine
the molecular defect has been identified as a chromosome 4 kinase mutations can underlie some of these CEL/myeloproliferative
27
deletion that yields a fusion gene encoding a FIP1LI/PDGFRA forms of HES. The presence of more than four myeloproliferative
(PDGF-α receptor) (F/P) protein that constitutively expresses features commonly seen in mutation-positive disease, predicted
receptor kinase activity. This fusion gene can be diagnostically response in those without known mutations. Some of these
evaluated by reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction features included dysplastic eosinophils, vitamin B 12 level >1000
(RT-PCR) or fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) (Chapter picograms per milliliter (pg/mL), tryptase level ≥12 nanograms
96). Importantly, the majority of patients with this fusion muta- per milliliter (ng/mL), anemia/thrombocytopenia, hypercellular
tion, which constitutes a form of chronic eosinophilic leukemia marrow, and spindled mast cells, reticulin fibrosis, and dysplastic
28
(CEL), respond to therapy with imatinib, which is considered megakaryocytes on bone marrow biopsy. In addition, clonal