Page 411 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 411
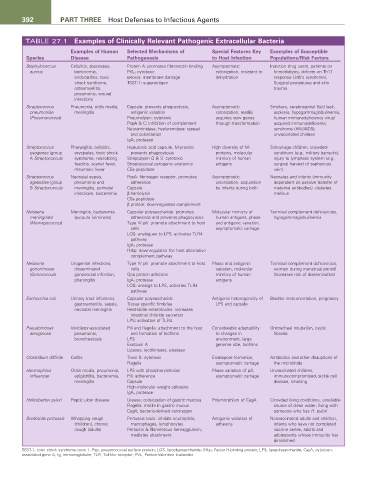
392 PARt tHREE Host Defenses to Infectious Agents
TABLE 27.1 Examples of Clinically Relevant Pathogenic Extracellular Bacteria
Examples of Human Selected Mechanisms of Special Features Key Examples of Susceptible
Species Disease Pathogenesis to Host Infection Populations/Risk Factors
Staphylococcus Cellulitis, abscesses, Protein A: promotes fibronectin binding Asymptomatic Injection drug users, patients on
aureus bacteremia, PVL: cytotoxic colonization, resistant to hemodialysis, defects on Th17
endocarditis, toxic α-toxin: membrane damage dehydration response (Job’s syndrome),
shock syndrome, TSST-1: superantigen Surgical procedures and skin
osteomyelitis, trauma
pneumonia, wound
infections
Streptococcus Pneumonia, otitis media, Capsule: prevents phagocytosis, Asymptomatic Smokers, cerebrospinal fluid leak,
pneumoniae meningitis antigenic variation colonization, readily asplenia, hypogammaglobulinemia,
(Pneumococcus) Pneumolysin: cytotoxic acquires new genes human immunodeficiency virus/
PspA & C: inhibition of complement through transformation acquired immunodeficiency
Neuraminidase, hyaluronidase: spread syndrome (HIV/AIDS),
and colonization unvaccinated children
IgA 1 protease
Streptococcus Pharyngitis, cellulitis, Hyaluronic acid capsule, M-protein: High diversity of M- School-age children, crowded-
pyogenes (group erysipelas, toxic shock prevents phagocytosis proteins, molecular conditions (e.g., military barracks),
A Streptococcus) syndrome, necrotizing Streptolysin O & S: cytotoxic mimicry of human injury to lymphatic system (e.g.,
fasciitis, scarlet fever, Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins antigens surgical harvest of saphenous
rheumatic fever C5a peptidase vein)
Streptococcus Neonatal sepsis, FbsA: fibrinogen receptor, promotes Asymptomatic Neonates and infants (immunity
agalactiae (group pneumonia and adherence colonization, acquisition dependent on passive transfer of
B Streptococcus) meningitis, perinatal Capsule by infants during birth maternal antibodies), diabetes
infections, bacteremia β-hemolysin mellitus
C5a peptidase
β protein: downregulates complement
Neisseria Meningitis, bacteremia Capsular polysaccharide: promotes Molecular mimicry of Terminal complement deficiencies,
meningitidis (purpura fulminans) adherence and prevents phagocytosis human antigens, phase hypogammaglobulinemia
(Meningococcus) Type IV pili: promote attachment to host and antigenic variation,
cells asymptomatic carriage
LOS: analogues to LPS, activates TLR4
pathway
IgA 1 protease
fHbp: downregulates the host alternative
complement pathway
Neisseria Urogenital infections, Type IV pili: promote attachment to host Phase and antigenic Terminal complement deficiencies,
gonorrhoeae disseminated cells variation, molecular women during menstrual period
(Gonococcus) gonococcal infection, Opa protein adhesion mimicry of human (increases risk of dissemination)
pharyngitis IgA 1 protease antigens
LOS: analogs to LPS, activates TLR4
pathway
Escherichia coli Urinary tract infections, Capsular polysaccharide Antigenic heterogeneity of Bladder instrumentation, pregnancy
gastroenteritis, sepsis, Tissue specific fimbriae LPS and capsule
neonatal meningitis Heat-labile enterotoxins: increases
intestinal chloride secretion
LPS: activation of TLR4
Pseudomonas Ventilator-associated Pili and flagella: attachment to the host Considerable adaptability Orotracheal intubation, cystic
aeruginosa pneumonia, and formation of biofilms to changes in fibrosis
bronchiectasis LPS environment, large
Exotoxin A genome size, biofilms
Lipases, lecithinases, elastase
Clostridium difficile Colitis Toxin B: cytotoxic Endospore formation, Antibiotics and other disruptions of
Flagella asymptomatic carriage the microbiotia
Haemophilus Otitis media, pneumonia, LPS with phosphorylcholine Phase variation of pili, Unvaccinated children,
influenzae epiglottitis, bacteremia, Pili: adherence asymptomatic carriage immunocompromised, sickle cell
meningitis Capsule disease, smoking
High-molecular weight adhesins
IgA 1 protease
Helicobacter pylori Peptic ulcer disease Urease: colonization of gastric mucosa Polymorphism of CagA Crowded living conditions, unreliable
Flagella: motile in gastric mucus source of clean water, living with
CagA; bacteria-derived carcinogen someone who has H. pylori
Bordetella pertussis Whopping cough Pertussis toxin: inhibits neutrophils, Antigenic variation of Nonvaccinated adults and children,
(children), chronic macrophages, lymphocytes adhesins infants who have not completed
cough (adults) Pertactin & filamentous hemagglutinin; vaccine series, adults and
mediates attachment adolescents whose immunity has
diminished
TSST-1, toxic shock syndrome toxin 1; Psp, pneumococcal surface protein; LOS, lipooligosaccharide; fHbp, Factor H-binding protein; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; CapA, cytotoxin-
associated gene A; Ig, immunoglobulin; TLR, Toll-like receptor; PVL, Panton-Valentine leukocidin.