Page 45 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 45
CHaPter 2 Organization of the Immune System 31
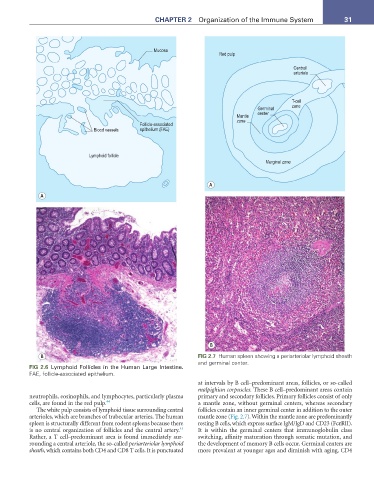
0XFRVD
Red pulp
Central
arteriole
T-cell
Germinal zone
Mantle center
)ROOLFOH DVVRFLDWHG zone
%ORRG YHVVHOV HSLWKHOLXP )$(
/\PSKRLG IROOLFOH
Marginal zone
A
A
B
B FIG 2.7 Human spleen showing a periarteriolar lymphoid sheath
and germinal center.
FIG 2.6 Lymphoid Follicles in the Human Large Intestine.
FAE, follicle-associated epithelium.
at intervals by B cell–predominant areas, follicles, or so-called
malpighian corpuscles. These B cell–predominant areas contain
neutrophils, eosinophils, and lymphocytes, particularly plasma primary and secondary follicles. Primary follicles consist of only
cells, are found in the red pulp. 44 a mantle zone, without germinal centers, whereas secondary
The white pulp consists of lymphoid tissue surrounding central follicles contain an inner germinal center in addition to the outer
arterioles, which are branches of trabecular arteries. The human mantle zone (Fig. 2.7). Within the mantle zone are predominantly
spleen is structurally different from rodent spleens because there resting B cells, which express surface IgM/IgD and CD23 (FcεRII).
44
is no central organization of follicles and the central artery. It is within the germinal centers that immunoglobulin class
Rather, a T cell–predominant area is found immediately sur- switching, affinity maturation through somatic mutation, and
rounding a central arteriole, the so-called periarteriolar lymphoid the development of memory B cells occur. Germinal centers are
sheath, which contains both CD4 and CD8 T cells. It is punctuated more prevalent at younger ages and diminish with aging. CD4