Page 476 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 476
CHaPTEr 32 Approach to the Evaluation of the Patient With Suspected Immunodeficiency 457
P1009: CD4 Oxidase activity can be detected by a flow cytometry assay
8000 measuring the oxidation of dihydrorhodamine (DHR) 123 in
19
phagocytes, resulting in fluorescent rhodamine-123. The
nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) test measures oxidative burst activity
6000
as well, but it is a more subjective test and can miss the diagnosis
of CGD. For patients with suspected LAD-1 deficiency, neutrophils
Counts 4000 are labeled with mAb directed against the adhesion molecule
CD11/CD18 heterodimer. Absence of fluorescence intensity
indicates lack of expression of the adhesion molecule. In addition,
2000 an increase of fluorescence intensity after stimulation can be
documented in normal individuals, indicating the normal
20
0 upregulation of this molecule after cell activation. Other labora-
0 5 10 15 tory techniques used to identify phagocytic defects include assays
for chemotaxis and bactericidal activity. A major pitfall for
Age (years) neutrophil studies is the spontaneous cell activation that might
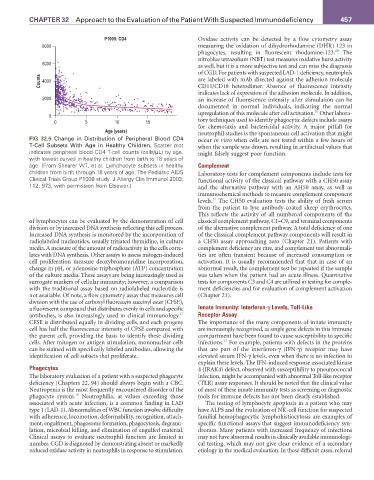
FIG 32.5 Change in Distribution of Peripheral Blood CD4 occur in vitro when cells are not tested within a few hours of
T-Cell Subsets With Age in Healthy Children. Scatter plot when the sample was drawn, resulting in artifactual values that
indicates peripheral blood CD4 T-cell counts (cells/µL) by age, might falsely suggest poor function.
with lowest curves in healthy children from birth to 18 years of
age. (From Shearer WT, et al. Lymphocyte subsets in healthy Complement
children from birth through 18 years of age: The Pediatric AIDS Laboratory tests for complement components include tests for
Clinical Trials Group P1009 study. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003; functional activity of the classical pathway with a CH50 assay
112: 973, with permission from Elsevier.) and the alternative pathway with an AH50 assay, as well as
immunochemical methods to measure complement component
21
levels. The CH50 evaluation tests the ability of fresh serum
from the patient to lyse antibody-coated sheep erythrocytes.
This reflects the activity of all numbered components of the
of lymphocytes can be evaluated by the demonstration of cell classical complement pathway, C1–C9, and terminal components
division or by increased DNA synthesis reflecting this cell process. of the alternative complement pathway. A total deficiency of one
Increased DNA synthesis is monitored by the incorporation of of the classical complement pathway components will result in
radiolabeled nucleotides, usually tritiated thymidine, in culture a CH50 assay approaching zero (Chapter 21). Patients with
media. A measure of the amount of radioactivity in the cells corre- complement deficiency are rare, and complement test abnormali-
lates with DNA synthesis. Other assays to assess mitogen-induced ties are often transient because of increased consumption or
cell proliferation measure deoxybromouridine incorporation, activation. It is usually recommended that that in case of an
change in pH, or adenosine triphosphate (ATP) concentration abnormal result, the complement test be repeated if the sample
of the culture media. These assays are being increasingly used as was taken when the patient had an acute illness. Quantitative
surrogate markers of cellular immunity; however, a comparison tests for components C3 and C4 are utilized in testing for comple-
with the traditional assay based on radiolabeled nucleotide is ment deficiencies and for evaluation of complement activation
not available. Of note, a flow cytometry assay that measures cell (Chapter 21).
division with the use of carboxyl fluorescein succinyl ester (CFSE),
a fluorescent compound that distributes evenly in cells and specific Innate Immunity: Interferon-γ Levels, Toll-Like
17
antibodies, is also increasingly used in clinical immunology. Receptor Assay
CFSE is distributed equally in dividing cells, and each progeny The importance of the many components of innate immunity
cell has half the fluorescence intensity of CFSE compared with are increasingly recognized, as single gene defects in this immune
the parent cell, providing the basis to identify these dividing compartment have been found to cause susceptibility to specific
22
cells. After mitogen or antigen stimulation, mononuclear cells infections. For example, patients with defects in the proteins
can be stained with specifically labeled antibodies, allowing the that are part of the interferon-γ (IFN-γ) receptor may have
identification of cell subsets that proliferate. elevated serum IFN-γ levels, even when there is no infection to
explain these levels. The IFN-induced response associated kinase
Phagocytes 4 (IRAK4) defect, observed with susceptibility to pneumococcal
The laboratory evaluation of a patient with a suspected phagocyte infection, might be accompanied with abnormal Toll-like receptor
deficiency (Chapters 22, 94) should always begin with a CBC. (TLR) assay responses. It should be noted that the clinical value
Neutropenia is the most frequently encountered disorder of the of most of these innate immunity tests as screening or diagnostic
18
phagocyte system. Neutrophilia, at values exceeding those tools for immune defects has not been clearly established.
associated with acute infection, is a common finding in LAD The testing of lymphocyte apoptosis in a patient who may
type 1 (LAD-1). Abnormalities of WBC function involve difficulty have ALPS and the evaluation of NK-cell function for suspected
with adherence, locomotion, deformability, recognition, attach- familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis are examples of
ment, engulfment, phagosome formation, phagocytosis, degranu- specific functional assays that suggest immunodeficiency syn-
lation, microbial killing, and elimination of engulfed material. dromes. Many patients with increased frequency of infections
Clinical assays to evaluate neutrophil function are limited in may not have abnormal results in clinically available immunologi-
number. CGD is diagnosed by demonstrating absent or markedly cal testing, which may not give clear evidence of a secondary
reduced oxidase activity in neutrophils in response to stimulation. etiology in the medical evaluation. In these difficult cases, referral