Page 576 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 576
CHaPTEr 39 HIV and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome 553
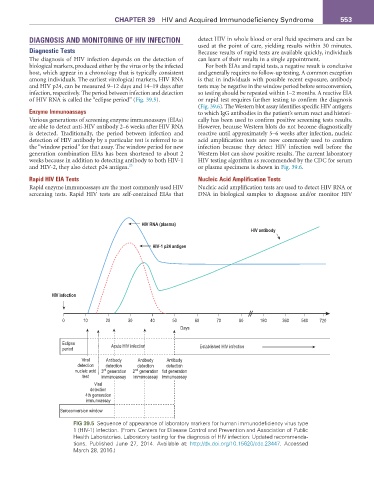
DIAGNOSIS AND MONITORING OF HIV INFECTION detect HIV in whole blood or oral fluid specimens and can be
used at the point of care, yielding results within 30 minutes.
Diagnostic Tests Because results of rapid tests are available quickly, individuals
The diagnosis of HIV infection depends on the detection of can learn of their results in a single appointment.
biological markers, produced either by the virus or by the infected For both EIAs and rapid tests, a negative result is conclusive
host, which appear in a chronology that is typically consistent and generally requires no follow-up testing. A common exception
among individuals. The earliest virological markers, HIV RNA is that in individuals with possible recent exposure, antibody
and HIV p24, can be measured 9–12 days and 14–19 days after tests may be negative in the window period before seroconversion,
infection, respectively. The period between infection and detection so testing should be repeated within 1–2 months. A reactive EIA
of HIV RNA is called the “eclipse period” (Fig. 39.5). or rapid test requires further testing to confirm the diagnosis
(Fig. 39.6). The Western blot assay identifies specific HIV antigens
Enzyme Immunoassays to which IgG antibodies in the patient’s serum react and histori-
Various generations of screening enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) cally has been used to confirm positive screening tests results.
are able to detect anti-HIV antibody 2–6 weeks after HIV RNA However, because Western blots do not become diagnostically
is detected. Traditionally, the period between infection and reactive until approximately 5–6 weeks after infection, nucleic
detection of HIV antibody by a particular test is referred to as acid amplification tests are now commonly used to confirm
the “window period” for that assay. The window period for new infection because they detect HIV infection well before the
generation combination EIAs has been shortened to about 2 Western blot can show positive results. The current laboratory
weeks because in addition to detecting antibody to both HIV-1 HIV testing algorithm as recommended by the CDC for serum
and HIV-2, they also detect p24 antigen. 23 or plasma specimens is shown in Fig. 39.6.
Rapid HIV EIA Tests Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests
Rapid enzyme immunoassays are the most commonly used HIV Nucleic acid amplification tests are used to detect HIV RNA or
screening tests. Rapid HIV tests are self-contained EIAs that DNA in biological samples to diagnose and/or monitor HIV
HIV RNA (plasma)
HIV antibody
HIV-1 p24 antigen
HIV infection
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 180 360 540 720
Days
Eclipse
period Acute HIV infection Established HIV infection
Viral Antibody Antibody Antibody
detection detection detection detection
nd
rd
nucleic acid 3 generation 2 generation 1st generation
test immunoassay immunoassay immunoassay
Viral
detection
4th generation
immunoassay
Seroconversion window
fIG 39.5 Sequence of appearance of laboratory markers for human immunodeficiency virus type
1 (HIV-1) infection. (From: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Association of Public
Health Laboratories. Laboratory testing for the diagnosis of HIV infection: Updated recommenda-
tions. Published June 27, 2014. Available at: http://dx.doi.org/10.15620/cdc.23447. Accessed
March 28, 2016.)