Page 577 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 577
554 ParT fOur Immunological Deficiencies
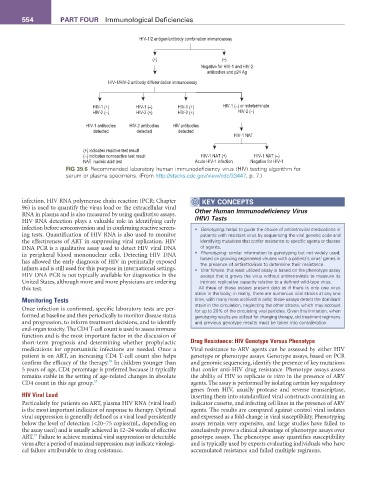
HIV-1/2 antigen/antibody combination immunoassay
(+) (–)
Negative for HIV-1 and HIV-2
antibodies and p24 Ag
HIV-1/HIV-2 antibody differentiation immunoassay
HIV-1 (+) HIV-1 (–) HIV-1 (+) HIV-1 (–) or indeterminate
HIV-2 (–) HIV-2 (+) HIV-2 (+) HIV-2 (–)
HIV-1 antibodies HIV-2 antibodies HIV antibodies
detected detected detected
HIV-1 NAT
(+) indicates reactive test result
(–) indicates nonreactive test result HIV-1 NAT (+) HIV-1 NAT (–)
NAT: nucleic acid test Acute HIV-1 infection Negative for HIV-1
fIG 39.6 Recommended laboratory human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) testing algorithm for
serum or plasma specimens. (From http://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/23447, p. 7.)
infection. HIV RNA polymerase chain reaction (PCR; Chapter KEY CONCEPTS
96) is used to quantify the virus load or the extracellular viral Other Human Immunodeficiency Virus
RNA in plasma and is also measured by using qualitative assays.
HIV RNA detection plays a valuable role in identifying early (HIV) Tests
infection before seroconversion and in confirming reactive screen- • Genotyping: helps to guide the choice of antiretroviral medications in
ing tests. Quantification of HIV RNA is also used to monitor patients with resistant virus by sequencing the viral genetic code and
the effectiveness of ART in suppressing viral replication. HIV identifying mutations that confer resistance to specific agents or classes
DNA PCR is a qualitative assay used to detect HIV viral DNA of agents.
in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Detecting HIV DNA • Phenotyping: similar information to genotyping but not widely used;
has allowed the early diagnosis of HIV in perinatally exposed based on growing engineered viruses with a patient’s virus’ genes in
the presence of antiretrovirals to determine their resistance.
infants and is still used for this purpose in international settings. • Viral fitness: this least utilized assay is based on the phenotype assay
HIV DNA PCR is not typically available for diagnostics in the except that it grows the virus without antiretrovirals to measure its
United States, although more and more physicians are ordering intrinsic replicative capacity relative to a defined wild-type virus.
this test. All three of these assays present data as if there is only one virus
strain in the body; in reality, there are numerous viral strains at any one
Monitoring Tests time, with many more archived in cells; these assays detect the dominant
strain in the circulation, neglecting the other strains, which may account
Once infection is confirmed, specific laboratory tests are per- for up to 20% of the circulating viral particles. Given this limitation, when
formed at baseline and then periodically to monitor disease status genotyping results are utilized for changing therapy, old treatment regimens
and progression, to inform treatment decisions, and to identify and previous genotype results must be taken into consideration.
end-organ toxicity. The CD4 T-cell count is used to assess immune
function and is the most important factor in the discussion of
short-term prognosis and determining whether prophylactic Drug Resistance: HIV Genotype Versus Phenotype
medications for opportunistic infections are needed. Once a Viral resistance to ARV agents can be assessed by either HIV
patient is on ART, an increasing CD4 T-cell count also helps genotype or phenotype assays. Genotype assays, based on PCR
24
confirm the efficacy of the therapy. In children younger than and genomic sequencing, identify the presence of key mutations
5 years of age, CD4 percentage is preferred because it typically that confer anti-HIV drug resistance. Phenotype assays assess
remains stable in the setting of age-related changes in absolute the ability of HIV to replicate in vitro in the presence of ARV
CD4 count in this age group. 25 agents. The assay is performed by isolating certain key regulatory
genes from HIV, usually protease and reverse transcriptase,
HIV Viral Load inserting them into standardized viral constructs containing an
Particularly for patients on ART, plasma HIV RNA (viral load) indicator cassette, and infecting cell lines in the presence of ARV
is the most important indicator of response to therapy. Optimal agents. The results are compared against control viral isolates
viral suppression is generally defined as a viral load persistently and expressed as a fold-change in viral susceptibility. Phenotyping
below the level of detection (<20–75 copies/mL, depending on assays remain very expensive, and large studies have failed to
the assay used) and is usually achieved in 12–24 weeks of effective conclusively prove a clinical advantage of phenotype assays over
24
ART. Failure to achieve maximal viral suppression or detectable genotype assays. The phenotype assay quantifies susceptibility
virus after a period of maximal suppression may indicate virologi- and is typically used by experts evaluating individuals who have
cal failure attributable to drug resistance. accumulated resistance and failed multiple regimens.