Page 685 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 685
658 ParT FivE Allergic diseases
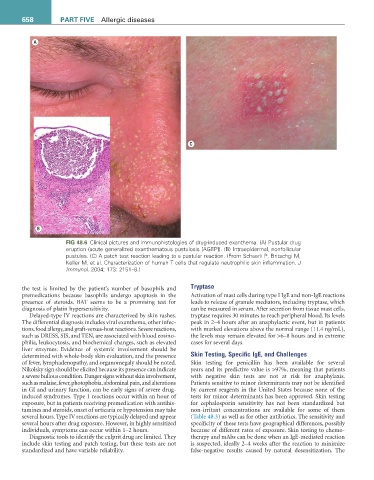
A
C
B
FiG 48.6 Clinical pictures and immunohistologies of drug-induced exanthema. (A) Pustular drug
eruption (acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis [AGEP]). (B) Intraepidermal, nonfollicular
pustules. (C) A patch test reaction leading to a pustular reaction. (From Schaerli P, Britschgi M,
Keller M, et al. Characterization of human T cells that regulate neutrophilic skin inflammation. J
Immunol. 2004; 173: 2151–8.)
Tryptase
the test is limited by the patient’s number of basophils and
premedications because basophils undergo apoptosis in the Activation of mast cells during type I IgE and non-IgE reactions
presence of steroids. BAT seems to be a promising test for leads to release of granule mediators, including tryptase, which
diagnosis of platin hypersensitivity. can be measured in serum. After secretion from tissue mast cells,
Delayed-type IV reactions are characterized by skin rashes. tryptase requires 30 minutes to reach peripheral blood. Its levels
The differential diagnosis includes viral exanthema, other infec- peak in 2–4 hours after an anaphylactic event, but in patients
tions, food allergy, and graft-versus-host reactions. Severe reactions, with marked elevations above the normal range (11.4 ng/mL),
such as DRESS, SJS, and TEN, are associated with blood eosino- the levels may remain elevated for >6–8 hours and in extreme
philia, leukocytosis, and biochemical changes, such as elevated cases for several days.
liver enzymes. Evidence of systemic involvement should be
determined with whole-body skin evaluation, and the presence Skin Testing, Specific IgE, and Challenges
of fever, lymphadenopathy, and organomegaly should be noted. Skin testing for penicillin has been available for several
Nikolsky sign should be elicited because its presence can indicate years and its predictive value is >97%, meaning that patients
a severe bullous condition. Danger signs without skin involvement, with negative skin tests are not at risk for anaphylaxis.
such as malaise, fever, photophobia, abdominal pain, and alterations Patients sensitive to minor determinants may not be identified
in GI and urinary function, can be early signs of severe drug- by current reagents in the United States because none of the
induced syndromes. Type 1 reactions occur within an hour of tests for minor determinants has been approved. Skin testing
exposure, but in patients receiving premedication with antihis- for cephalosporin sensitivity has not been standardized but
tamines and steroids, onset of urticaria or hypotension may take non-irritant concentrations are available for some of them
several hours. Type IV reactions are typically delayed and appear (Table 48.3) as well as for other antibiotics. The sensitivity and
several hours after drug exposure. However, in highly sensitized specificity of these tests have geographical differences, possibly
individuals, symptoms can occur within 1–2 hours. because of different rates of exposure. Skin testing to chemo-
Diagnostic tools to identify the culprit drug are limited. They therapy and mAbs can be done when an IgE-mediated reaction
include skin testing and patch testing, but these tests are not is suspected, ideally 2–4 weeks after the reaction to minimize
standardized and have variable reliability. false-negative results caused by natural desensitization. The