Page 687 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 687
660 ParT FivE Allergic diseases
H H
ROCHN S ROCHN S R H H H
N N N S
O O X O N
CO 2 H CO H O
2
Penicillins Cephalosporins CO Na
2
NH 2
O OH Carrier
R 1 S protein
R N
N O Hydrolysis
O CO 2 H
CO 2 H
Clavulanic acid
Penems (an oxapenem)
H H H S
R N
H RHN N CO Na
HO O H 2
R HN O Penicilloyl
N N –
O O SO 3 Carrier
CO 2 H
Carbapenems Monobactams protein
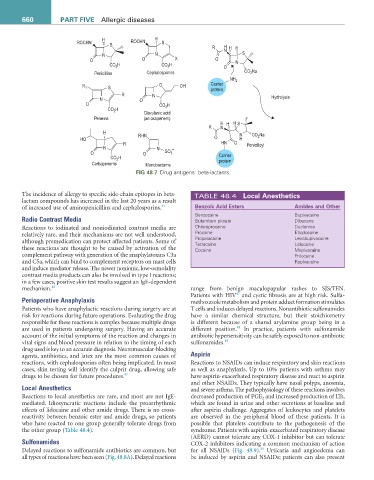
FiG 48.7 Drug antigens: beta-lactams.
The incidence of allergy to specific side-chain epitopes in beta- TABLE 48.4 Local anesthetics
lactam compounds has increased in the last 20 years as a result
of increased use of aminopenicillins and cephalosporins. 44 Benzoic acid Esters amides and Other
Benzocaine Bupivacaine
Radio Contrast Media Butamben picrate Dibucane
Reactions to iodinated and noniodinated contrast media are Chloroprocaine Duclonine
relatively rare, and their mechanisms are not well understood, Procaine Etiodocaine
although premedication can protect affected patients. Some of Proparacaine Levobupivacaine
Tetracaine
Lidocaine
these reactions are thought to be caused by activation of the Cocaine Mepivacaine
complement pathway with generation of the anaphylatoxins C3a Prilocaine
and C5a, which can bind to complement receptors on mast cells Ropivacaine
and induce mediator release. The newer nonionic, low-osmolality
contrast media products can also be involved in type I reactions;
in a few cases, positive skin test results suggest an IgE-dependent
mechanism. 45 range from benign maculopapular rashes to SJS/TEN.
47
Patients with HIV and cystic fibrosis are at high risk. Sulfa-
Perioperative Anaphylaxis methoxazole metabolism and protein adduct formation stimulates
Patients who have anaphylactic reactions during surgery are at T cells and induces delayed reactions. Nonantibiotic sulfonamides
risk for reactions during future operations. Evaluating the drug have a similar chemical structure, but their stoichiometry
responsible for these reactions is complex because multiple drugs is different because of a shared arylamine group being in a
48
are used in patients undergoing surgery. Having an accurate different position. In practice, patients with sulfonamide
account of the initial symptoms of the reaction and changes in antibiotic hypersensitivity can be safely exposed to non-antibiotic
vital signs and blood pressure in relation to the timing of each sulfonamides. 49
drug used is key to an accurate diagnosis. Neuromuscular-blocking
agents, antibiotics, and latex are the most common causes of Aspirin
reactions, with cephalosporins often being implicated. In most Reactions to NSAIDs can induce respiratory and skin reactions
cases, skin testing will identify the culprit drug, allowing safe as well as anaphylaxis. Up to 10% patients with asthma may
drugs to be chosen for future procedures. 47 have aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease and react to aspirin
and other NSAIDs. They typically have nasal polyps, anosmia,
Local Anesthetics and severe asthma. The pathophysiology of these reactions involves
Reactions to local anesthetics are rare, and most are not IgE- decreased production of PGE 2 and increased production of LTs,
mediated. Idiosyncratic reactions include the proarrhythmic which are found in urine and other secretions at baseline and
effects of lidocaine and other amide drugs. There is no cross- after aspirin challenge. Aggregates of leukocytes and platelets
reactivity between benzoic ester and amide drugs, so patients are observed in the peripheral blood of these patients. It is
who have reacted to one group generally tolerate drugs from possible that platelets contribute to the pathogenesis of the
the other group (Table 48.4). syndrome. Patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease
(AERD) cannot tolerate any COX-1 inhibitor but can tolerate
Sulfonamides COX-2 inhibitors indicating a common mechanism of action
50
Delayed reactions to sulfonamide antibiotics are common, but for all NSAIDs (Fig. 48.9). Urticaria and angioedema can
all types of reactions have been seen (Fig. 48.8A). Delayed reactions be induced by aspirin and NSAIDs; patients can also present