Page 847 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 847
CHaPtEr 59 Large-Vessel Vasculitides 819
$ %
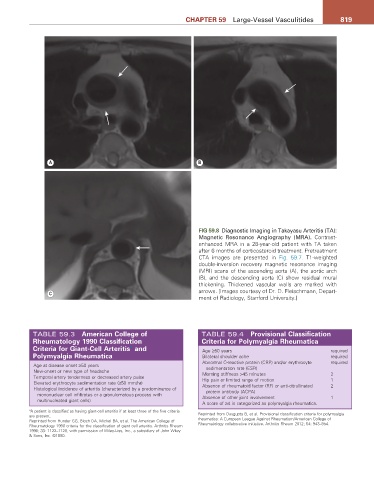
FIG 59.8 Diagnostic Imaging in Takayasu Arteritis (TA):
Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA). Contrast-
enhanced MRA in a 28-year-old patient with TA taken
after 6 months of corticosteroid treatment. Pretreatment
CTA images are presented in Fig. 59.7. T1-weighted
double-inversion recovery magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI) scans of the ascending aorta (A), the aortic arch
(B), and the descending aorta (C) show residual mural
thickening. Thickened vascular walls are marked with
& arrows. [Images courtesy of Dr. D. Fleischmann, Depart-
ment of Radiology, Stanford University.]
TABLE 59.3 american College of TABLE 59.4 Provisional Classification
rheumatology 1990 Classification Criteria for Polymyalgia rheumatica
Criteria for Giant-Cell arteritis and Age ≥50 years required
a
Polymyalgia rheumatica Bilateral shoulder ache required
Abnormal C-reactive protein (CRP) and/or erythrocyte required
Age at disease onset ≥50 years sedimentation rate (ESR)
New-onset or new type of headache Morning stiffness >45 minutes 2
Temporal artery tenderness or decreased artery pulse Hip pain or limited range of motion 1
Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (≥50 mm/hr) Absence of rheumatoid factor (RF) or anti-citrullinated 2
Histological incidence of arteritis (characterized by a predominance of protein antibody (ACPA)
mononuclear cell infiltrates or a granulomatous process with Absence of other joint involvement 1
multinucleated giant cells)
A score of ≥4 is categorized as polymyalgia rheumatica.
a A patient is classified as having giant-cell arteritis if at least three of the five criteria
are present. Reprinted from Dasgupta B, et al. Provisional classification criteria for polymyalgia
Reprinted from Hunder GG, Bloch DA, Michel BA, et al. The American College of rheumatica: A European League Against Rheumatism/American College of
Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum Rheumatology collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 2012; 64: 943–954.
1990; 33: 1122–1128, with permission of Wiley-Liss, Inc., a subsidiary of John Wiley
& Sons, Inc. ©1990.