Page 996 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 996
CHaPter 71 Type 1 Diabetes 961
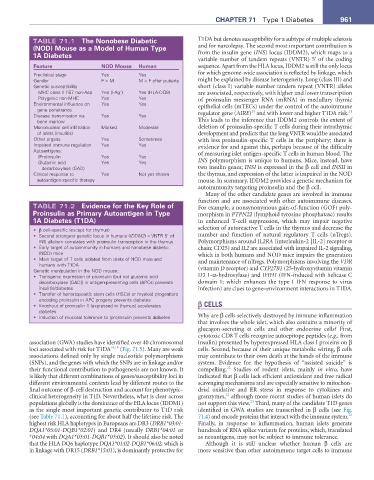
TABLE 71.1 the nonobese Diabetic T1DA but denotes susceptibility for a subtype of multiple sclerosis
(nOD) Mouse as a Model of Human type and for narcolepsy. The second most important contribution is
1a Diabetes from the insulin gene (INS) locus (IDDM2), which maps to a
variable number of tandem repeats (VNTR) 5’ of the coding
Feature nOD Mouse Human sequence. Apart from the HLA locus, IDDM2 is still the only locus
Preclinical stage Yes Yes for which genome-wide association is reflected by linkage, which
Gender F > M M > F after puberty might be explained by disease heterogeneity. Long (class III) and
Genetic susceptibility short (class I) variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) alleles
MHC class II fi57 non-Asp Yes (I-Ag ) Yes (HLA-DQ8) are associated, respectively, with higher and lower transcription
7
Polygenic non-MHC Yes Yes of proinsulin messenger RNA (mRNA) in medullary thymic
Environmental influence on Yes Yes epithelial cells (mTECs) under the control of the autoimmune
gene penetrance 20 21
Disease transmission via Yes Yes regulator gene (AIRE) and with lower and higher T1DA risk.
bone marrow This leads to the inference that IDDM2 controls the extent of
Mononuclear cell infiltration Marked Moderate deletion of proinsulin-specific T cells during their intrathymic
of islets (insulitis) development and predicts that the long VNTR would be associated
Other organs Yes Sometimes with less proinsulin-specific T cells in the periphery; there is
Impaired immune regulation Yes Yes evidence for and against this, perhaps because of the difficulty
Autoantigens: of measuring islet antigen-specific T cells in human blood. The
(Pro)insulin Yes Yes
Glutamic acid Yes Yes INS polymorphism is unique to humans. Mice, instead, have
decarboxylase (GAD) two insulin genes; INSI is expressed in the β cell and INSII in
Clinical response to Yes Not yet shown the thymus, and expression of the latter is impaired in the NOD
autoantigen-specific therapy mouse. In summary, IDDM2 provides a genetic mechanism for
autoimmunity targeting proinsulin and the β cell.
Many of the other candidate genes are involved in immune
function and are associated with other autoimmune diseases.
TABLE 71.2 evidence for the Key role of For example, a nonsynonymous gain-of-function (GOF) poly-
Proinsulin as Primary autoantigen in type morphism in PTPN22 (lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase) results
1a Diabetes (t1Da) in enhanced T-cell suppression, which may impair negative
• β cell–specific (except for thymus) selection of autoreactive T cells in the thymus and decrease the
• Second strongest genetic locus in humans (IDDM2) = VNTR 5’ of number and function of natural regulatory T cells (nTregs).
INS allelism correlates with proinsulin transcription in the thymus Polymorphisms around IL2RA (interleukin-2 [IL-2] receptor α
• Early target of autoimmunity in humans and nonobese diabetic chain; CD25) and IL2 are associated with impaired IL-2 signaling,
(NOD) mice which in both humans and NOD mice impairs the generation
• Main target of T cells isolated from islets of NOD mice and and maintenance of nTregs. Polymorphisms involving the VDR
humans with T1DA
Genetic manipulation in the NOD mouse: (vitamin D receptor) and CYP27B1 (25-hydroxyvitamin vitamin
• Transgenic expression of proinsulin (but not glutamic acid D3 1-α-hydroxylase) and IFIH1 (IFN-induced with helicase C
decarboxylase [GAD]) in antigen-presenting cells (APCs) prevents domain 1; which enhances the type I IFN response to virus
insulitis/diabetes infection) are clues to gene–environment interactions in T1DA.
• Transfer of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) or myeloid progenitors
encoding proinsulin in APC progeny prevents diabetes
• Knockout of proinsulin II (expressed in thymus) accelerates β CELLS
diabetes
• Induction of mucosal tolerance to (pro)insulin prevents diabetes Why are β cells selectively destroyed by immune inflammation
that involves the whole islet, which also contains a minority of
glucagon-secreting α cells and other endocrine cells? First,
cytotoxic CD8 T cells recognize autoepitope peptides (e.g., from
association (GWA) studies have identified over 40 chromosomal insulin) presented by hyperexpressed HLA class I proteins on β
loci associated with risk for T1DA 18,19 (Fig. 71.5). Many are weak cells. Second, because of their unique metabolic wiring, β cells
associations defined only by single nucleotide polymorphisms may contribute to their own death at the hands of the immune
(SNPs), and the genes with which the SNPs are in linkage and/or system. Evidence for the hypothesis of “assisted suicide” is
22
their functional contribution to pathogenesis are not known. It compelling. Studies of rodent islets, mainly in vitro, have
is likely that different combinations of genes/susceptibility loci in indicated that β cells lack efficient antioxidant and free radical
different environmental contexts lead by different routes to the scavenging mechanisms and are especially sensitive to mitochon-
final outcome of β-cell destruction and account for phenotypic– drial oxidative and ER stress in response to cytokines and
22
clinical heterogeneity in T1D. Nevertheless, what is clear across granzymes, although more recent studies of human islets do
23
populations globally is the dominance of the HLA locus (IDDM1) not support this view. Third, many of the candidate T1D genes
as the single most important genetic contributor to T1D risk identified in GWA studies are transcribed in β cells (see Fig.
23
(see Table 71.1), accounting for about half the lifetime risk. The 71.4) and encode proteins that interact with the immune system.
highest risk HLA haplotypes in Europeans are DR3 (DRB1*03:01- Finally, in response to inflammation, human islets generate
DQA1*05:01-DQB1*02:01) and DR4 (usually DRB1*04:01 or hundreds of RNA splice variants for proteins, which, translated
*04:04 with DQA1*03:01-DQB1*03:02). It should also be noted as neoantigens, may not be subject to immune tolerance.
that the HLA DQ6 haplotype DQA1*01:02-DQB1*06:02, which is Although it is still unclear whether human β cells are
in linkage with DR15 (DRB1*15:01), is dominantly protective for more sensitive than other autoimmune target cells to immune