Page 997 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 997
962 Part seven Organ-Specific Inflammatory Disease
7.0
6.5
6.0
Odds ratio 5.5
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
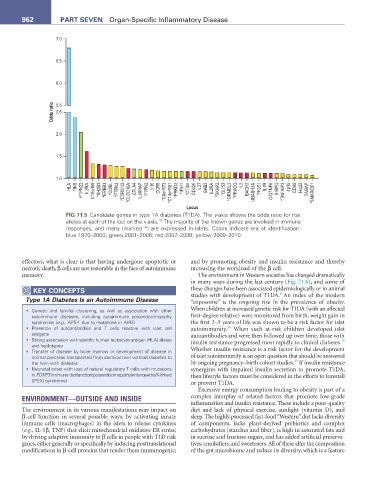
HLA *INS PTPN22 IL2RA C10orf59 *SH2B3 *ERBB3 *COBL *PTPN2 *CTRB1/2 *CLEC16A CTLA4 IL18RAP PTPN2 IL10 CCR5 *C6orf173 *C14orf181 *PRKD2 *IFIH1 *CTSH CD226 IL27 GAB3 IL2RA *SKAP2 *GLIS3 *ORMDL3 *PRKCQ IL2 BACH2 UBASH3A *RGS1 IL7R CIQTNF6 SIRPG *TNFAIP3 4p15 CD69 14q22 TAGAP *SMARCE1
Locus
FIG 71.5 Candidate genes in type 1A diabetes (T1DA). The y-axis shows the odds ratio for risk
alleles at each of the loci on the x-axis. The majority of the known genes are involved in immune
18
responses, and many (marked *) are expressed in islets. Colors indicate era of identification:
blue 1970–2000; green 2001–2006; red 2007–2008; yellow 2009–2010.
effectors, what is clear is that having undergone apoptotic or and by promoting obesity and insulin resistance and thereby
necrotic death, β cells are not restorable in the face of autoimmune increasing the workload of the β cell.
memory. The environment in Western societies has changed dramatically
in many ways during the last century (Fig. 71.6), and some of
KeY COnCePts these changes have been associated epidemiologically or in animal
6
Type 1A Diabetes Is an Autoimmune Disease studies with development of T1DA. An index of the modern
“exposome” is the ongoing rise in the prevalence of obesity.
• Genetic and familial clustering, as well as association with other When children at increased genetic risk for T1DA (with an affected
autoimmune diseases, including autoimmune polyendocrinopathy first-degree relative) were monitored from birth, weight gain in
syndromes (e.g., APS-1 due to mutations in AIRE) the first 2–3 years of life was shown to be a risk factor for islet
• Presence of autoantibodies and T cells reactive with islet cell autoimmunity. When such at-risk children developed islet
24
antigens autoantibodies and were then followed up over time, those with
• Strong association with specific human leukocyte antigen (HLA) alleles insulin resistance progressed most rapidly to clinical diabetes.
15
and haplotypes
• Transfer of disease by bone marrow or development of disease in Whether insulin resistance is a risk factor for the development
normal pancreas transplanted from identical twin without diabetes to of islet autoimmunity is an open question that should be answered
25
the twin with diabetes by ongoing pregnancy–birth cohort studies. If insulin resistance
• Neonatal onset with loss of natural regulatory T cells with mutations synergizes with impaired insulin secretion to promote T1DA,
in FOXP3 (immune dysfunction/polyendocrinopathy/enteropathy/X-linked then lifestyle factors must be considered in the efforts to forestall
[IPEX] syndrome) or prevent T1DA.
Excessive energy consumption leading to obesity is part of a
ENVIRONMENT—OUTSIDE AND INSIDE complex interplay of related factors that promote low-grade
inflammation and insulin resistance. These include a poor-quality
The environment in its various manifestations may impact on diet and lack of physical exercise, sunlight (vitamin D), and
β-cell function in several possible ways: by activating innate sleep. The highly processed fast-food “Western” diet lacks diversity
immune cells (macrophages) in the islets to release cytokines of components, lacks plant-derived prebiotics and complex
(e.g., IL-1β, TNF) that elicit mitochondrial oxidative ER stress; carbohydrates (starches and fiber), is high in saturated fats and
by driving adaptive immunity to β cells in people with T1D risk in sucrose and fructose sugars, and has added artificial preserva-
genes, either generally or specifically by inducing posttranslational tives, emulsifiers, and sweeteners. All of these alter the composition
modifications in β-cell proteins that render them immunogenic; of the gut microbiome and reduce its diversity, which is a feature