Page 1357 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1357
930 PART 8: Renal and Metabolic Disorders
preferable to intermittent bolus administration. However, a recent 5
141
randomized controlled trial which compared bolus versus infusion Dopamine
of furosemide in 308 patients with acute decompensated heart failure Placebo
showed no difference in the patient’s global assessment of symptoms or 4
change in creatinine from baseline to 72 hours between the two groups. 142
Mannitol is an osmotic diuretic that can decrease cell swelling, scavenge
free radicals, and cause renal vasodilatation by inducing intrarenal pros- 3
taglandin production. It may be beneficial when added to organ pres- Serum creatinine (mg/dL)
143
ervation solutions during renal transplantation and may protect against 2
AKI caused by rhabdomyolysis if given extremely early. 143-145 Otherwise,
mannitol has not been shown to be useful in the prevention of AKI. In fact,
mannitol may aggravate AKI due to radiocontrast agents. Furthermore, 1
61
mannitol may precipitate pulmonary edema if given to volume-overloaded
patients who remain oliguric, can exacerbate the hyperosmolar state of
azotemia, and may even cause acute renal failure (“osmotic nephrosis”). 146 0 Peak SCr SCr Increase
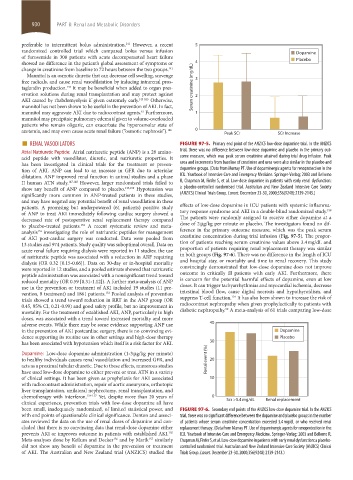
■ RENAL VASODILATORS FIGURE 97-5. Primary end point of the ANZICS low-dose dopamine trial. In the ANZICS
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide: Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) is a 28 amino- trial, there was no difference between low-dose dopamine and placebo in the primary out-
acid peptide with vasodilator, diuretic, and natriuretic properties. It come measure, which was peak serum creatinine attained during trial drug infusion. Peak
has been investigated in clinical trials for the treatment or preven- urea and increments from baseline of creatinine and urea were also similar in the placebo and
tion of AKI. ANP can lead to an increase in GFR due to arteriolar dopamine groups. (Data from Murray PT. Use of dopaminergic agents for renoprotection in the
dilatation. ANP improved renal function in animal studies and a phase ICU. Yearbook of Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine. Springer-Verlag; 2003 and Bellomo
II human ATN study. 147,148 However, larger randomized trials failed to R, Chapman M, Finfer S, et al. Low-dose dopamine in patients with early renal dysfunction:
show any benefit of ANP compared to placebo. 149,150 Hypotension was a placebo-controlled randomised trial. Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Society
significantly more common in ANP-treated patients in these studies, (ANZICS) Clinical Trials Group. Lancet. December 23-30, 2000;356(9248):2139-2143.)
and may have negated any potential benefit of renal vasodilation in these
patients. A promising but underpowered (61 patients) positive study effects of low-dose dopamine in ICU patients with systemic inflamma-
158
of ANP to treat AKI immediately following cardiac surgery showed a tory response syndrome and AKI in a double-blind randomized study.
decreased rate of postoperative renal replacement therapy compared The patients were randomly assigned to receive either dopamine at a
to placebo-treated patients. A recent systematic review and meta- dose of 2 µg/kg per minute or placebo. The investigators found no dif-
151
152
analysis investigating the role of natriuretic peptides for management ference in the primary outcome measure, which was the peak serum
of AKI post-cardiac surgery was conducted. Data were pooled from creatinine concentration during trial infusion (Fig. 97-5). The propor-
13 studies and 974 patients. Study quality was suboptimal overall. Data on tion of patients reaching serum creatinine values above 3.4 mg/dL and
acute renal failure requiring dialysis were reported in 11 studies; the use proportion of patients requiring renal replacement therapy was similar
of natriuretic peptide was associated with a reduction in ARF requiring in both groups (Fig. 97-6). There was no difference in the length of ICU
dialysis (OR 0.32 [0.15-0.66]). Data on 30-day or in-hospital mortality and hospital stay, or mortality and time to renal recovery. This study
were reported in 12 studies, and a pooled estimate showed that natriuretic convincingly demonstrated that low-dose dopamine does not improve
peptide administration was associated with a nonsignificant trend toward outcome in critically ill patients with early AKI. Furthermore, there
reduced mortality (OR 0.59 [0.31-1.12]). A further meta-analysis of ANP is concern for the potential harmful effects of dopamine, even at low
use in the prevention or treatment of AKI included 19 studies (11 pre- doses. It can trigger tachyarrhythmias and myocardial ischemia, decrease
vention, 8 treatment) and 1861 patients. Pooled analysis of prevention intestinal blood flow, cause digital necrosis and hypothyroidism, and
153
154
trials showed a trend toward reduction in RRT in the ANP group (OR suppress T-cell function. It has also been shown to increase the risk of
0.45, 95% CI, 0.21-0.99) and good safety profile, but no improvement in radiocontrast nephropathy when given prophylactically to patients with
59
mortality. For the treatment of established AKI, ANP, particularly in high diabetic nephropathy. A meta-analysis of 61 trials comparing low-dose
doses, was associated with a trend toward increased mortality and more
adverse events. While there may be some evidence supporting ANP use 40
in the prevention of AKI postcardiac surgery, there is no convincing evi- Dopamine
dence supporting its routine use in other settings and high-dose therapy Placebo
has been associated with hypotension which itself is a risk factor for AKI. 30
Dopamine: Low-dose dopamine administration (1-3 µg/kg per minute)
to healthy individuals causes renal vasodilation and increased GFR, and Renal event (%) 20
acts as a proximal tubular diuretic. Due to these effects, numerous studies
have used low-dose dopamine to either prevent or treat ATN in a variety
of clinical settings. It has been given as prophylaxis for AKI associated 10
with radiocontrast administration, repair of aortic aneurysms, orthotopic
liver transplantation, unilateral nephrectomy, renal transplantation, and
chemotherapy with interferon. 154-157 Yet, despite more than 20 years of 0
clinical experience, prevention trials with low-dose dopamine all have Scr >3.4 mg/dL Renal replacement
been small, inadequately randomized, of limited statistical power, and FIGURE 97-6. Secondary end points of the ANZICS low-dose dopamine trial. In the ANZICS
with end points of questionable clinical significance. Denton and associ- trial, there was no significant difference between the dopamine and placebo groups in the number
ates reviewed the data on the use of renal doses of dopamine and con- of patients whose serum creatinine concentration exceeded 3.4 mg/dL or who received renal
cluded that there is no convincing data that renal-dose dopamine either replacement therapy. (Data from Murray PT. Use of dopaminergic agents for renoprotection in the
prevents AKI or improves outcome in patients with established AKI. ICU. Yearbook of Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine. Springer-Verlag; 2003 and Bellomo R,
155
Meta-analyses done by Kellum and Decker and by Marik similarly Chapman M, Finfer S, et al. Low-dose dopamine in patients with early renal dysfunction: a placebo-
157
156
did not show any benefit of dopamine in the prevention or treatment controlled randomised trial. Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Society (ANZICS) Clinical
of AKI. The Australian and New Zealand trial (ANZICS) studied the Trials Group. Lancet. December 23-30, 2000;356(9248):2139-2143.)
section08.indd 930 1/14/2015 8:27:58 AM