Page 621 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 621
CHAPTER 29 ■ Body Fluid Analysis 605
Although aspiration was once per ormed in surgery, it is
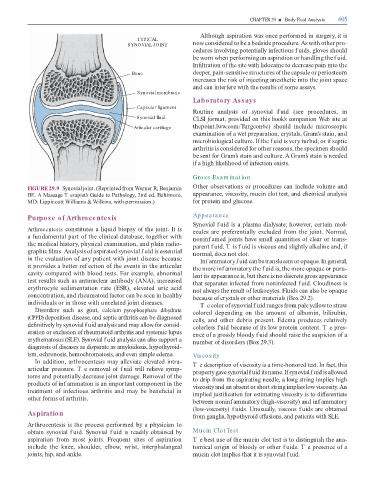
TYPICAL
SYNOVIAL JOINT now considered to be a bedside procedure. As with other pro-
cedures involving potentially in ectious f uids, gloves should
be worn when per orming an aspiration or handling the f uid.
In ltration o the site with lidocaine to decrease pain into the
Bone deeper, pain-sensitive structures o the capsule or periosteum
increases the risk o injecting anesthetic into the joint space
and can inter ere with the results o some assays.
Synovial membrane
Laboratory Assays
Capsular ligament
Routine analysis o synovial f uid (see procedures, in
Synovial fluid CLSI ormat, provided on this book’s companion Web site at
Articular cartilage thepoint.lww.com/ urgeon6e) should include microscopic
examination o a wet preparation, crystals, Gram’s stain, and
microbiological culture. I the f uid is very turbid, or i septic
arthritis is considered or other reasons, the specimen should
be sent or Gram’s stain and culture. A Gram’s stain is needed
i a high likelihood o in ection exists.
Gross Exam ination
FIGURE 29.9 Synovial joint. (Reprinted rom Werner R, Benjamin Other observations or procedures can include volume and
BE. A Massage T erapist’s Guide to Pathology, 2nd ed, Baltimore, appearance, viscosity, mucin clot test, and chemical analysis
MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, with permission.) or protein and glucose.
Purpose of Arthrocentesis Appearance
Synovial f uid is a plasma dialysate; however, certain mol-
Arthrocentesis constitutes a liquid biopsy o the joint. It is ecules are pre erentially excluded rom the joint. Normal,
a undamental part o the clinical database, together with noninf amed joints have small quantities o clear or trans-
the medical history, physical examination, and plain radio- parent f uid. T is f uid is viscous and slightly alkaline and, i
graphic lms. Analysis o aspirated synovial f uid is essential normal, does not clot.
in the evaluation o any patient with joint disease because Inf ammatory f uid can be translucent or opaque. In general,
it provides a better ref ection o the events in the articular the more inf ammatory the f uid is, the more opaque or puru-
cavity compared with blood tests. For example, abnormal lent its appearance is, but there is no discrete gross appearance
test results such as antinuclear antibody (ANA), increased that separates in ected rom nonin ected f uid. Cloudiness is
erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), elevated uric acid not always the result o leukocytes. Fluids can also be opaque
concentration, and rheumatoid actor can be seen in healthy because o crystals or other materials (Box 29.2).
individuals or in those with unrelated joint diseases. T e color o synovial f uid ranges rom pale yellow to straw
Disorders such as gout, calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate colored depending on the amount o albumin, bilirubin,
(CPPD) deposition disease, and septic arthritis can be diagnosed cells, and other debris present. Edema produces relatively
de nitively by synovial f uid analysis and may allow or consid- colorless f uid because o its low protein content. T e pres-
eration or exclusion o rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus ence o a grossly bloody f uid should raise the suspicion o a
erythematosus (SLE). Synovial f uid analysis can also support a number o disorders (Box 29.3).
diagnosis o diseases as disparate as amyloidosis, hypothyroid-
ism, ochronosis, hemochromatosis, and even simple edema. Viscosity
In addition, arthrocentesis may alleviate elevated intra- T e description o viscosity is a time-honored test. In act, this
articular pressure. T e removal o f uid will relieve symp- property gave synovial f uid its name. I synovial f uid is allowed
toms and potentially decrease joint damage. Removal o the to drip rom the aspirating needle, a long string implies high
products o inf ammation is an important component in the viscosity and an absent or short string implies low viscosity. An
treatment o in ectious arthritis and may be bene cial in implied justi cation or estimating viscosity is to di erentiate
other orms o arthritis.
between noninf ammatory (high-viscosity) and inf ammatory
(low-viscosity) f uids. Unusually, viscous f uids are obtained
Aspiration rom ganglia, hypothyroid e usions, and patients with SLE.
Arthrocentesis is the process per ormed by a physician to
obtain synovial f uid. Synovial f uid is readily obtained by Mucin Clot Test
aspiration rom most joints. Frequent sites o aspiration T e best use o the mucin clot test is to distinguish the ana-
include the knee, shoulder, elbow, wrist, interphalangeal tomical origin o bloody or other f uids. T e presence o a
joints, hip, and ankle. mucin clot implies that it is synovial f uid.