Page 619 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 619
CHAPTER 29 ■ Body Fluid Analysis 603
Peritoneal cavity
Peritoneum
Superior surface (roof) Urinary bladder
of bladder
Ureteric orifice
Supravesical fossa
Rectovesical pouch
Median umbilical ligament
Transverse rectal fold
Apex of bladder Internal urethral orifice
Linea alba Ampulla of rectum
Rectovesical septum
Pubic symphysis
Retropubic space/fat pad Prostate
Intramural part of urethra Prostatic utricle
Fundiform ligament of penis Prostatic and
intermediate urethra
Puboprostatic ligament
Perineal membrane
Suspensory ligament of penis
External urethral sphincter External anal sphincter
Spongy urethra Anal canal
Internal anal sphincter
Glans penis
Navicular fossa
Prepuce Head of epididymis
External urethral opening
Testis
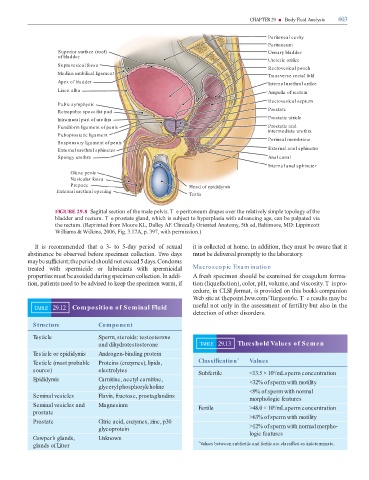
FIGURE 29.8 Sagittal section o the male pelvis. T e peritoneum drapes over the relatively simple topology o the
bladder and rectum. T e prostate gland, which is subject to hyperplasia with advancing age, can be palpated via
the rectum. (Reprinted rom Moore KL, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 5th ed, Baltimore, MD: Lippincott
Williams & Wilkins, 2006, Fig. 3.17A, p. 397, with permission.)
It is recommended that a 3- to 5-day period o sexual it is collected at home. In addition, they must be aware that it
abstinence be observed be ore specimen collection. wo days must be delivered promptly to the laboratory.
may be su cient; the period should not exceed 5 days. Condoms
treated with spermicide or lubricants with spermicidal Macroscopic Exam ination
properties must be avoided during specimen collection. In addi- A resh specimen should be examined or coagulum orma-
tion, patients need to be advised to keep the specimen warm, i tion (lique action), color, pH, volume, and viscosity. Tis pro-
cedure, in CLSI ormat, is provided on this book’s companion
Web site at thepoint.lww.com/ urgeon6e. T e results may be
TABLE 29.12 Composition of Seminal Fluid use ul not only in the assessment o ertility but also in the
detection o other disorders.
Structure Component
Testicle Sperm, steroids: testosterone
and dihydrotestosterone TABLE 29.13 Threshold Values of Semen
Testicle or epididymis Androgen-binding protein
Testicle (most probable Proteins (enzymes), lipids, Classi cation * Values
source) electrolytes
Subfertile <13.5 × 10 /mL sperm concentration
6
Epididymis Carnitine, acetyl carnitine, <32% of sperm with motility
glyceryl phosphorylcholine
<9% of sperm with normal
Seminal vesicles Flavin, fructose, prostaglandins morphologic features
Seminal vesicles and Magnesium Fertile >48.0 × 10 /mL sperm concentration
6
prostate
>63% of sperm with motility
Prostate Citric acid, enzymes, zinc, p30
glycoprotein >12% of sperm with normal morpho-
logic features
Cowper’s glands, Unknown
glands of Litter * Values between subfertile and fertile are classi ed as indeterminate.