Page 673 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 673
CHAPTER 31 ■ Molecular Diagnostic Techniques and Applications 657
which anneals between orward and reverse primers.
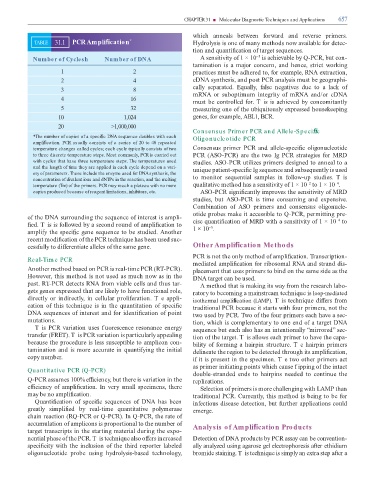
TABLE 31.1 PCR Ampli cation * Hydrolysis is one o many methods now available or detec-
tion and quanti cation o target sequences.
−5
Number of Cyclesh Number of DNA A sensitivity o 1 × 10 is achievable by Q-PCR, but con-
tamination is a major concern, and hence, strict working
1 2 practices must be adhered to, or example, RNA extraction,
2 4 cDNA synthesis, and post PCR analysis must be geographi-
cally separated. Equally, alse negatives due to a lack o
3 8
mRNA or suboptimum integrity o mRNA and/or cDNA
4 16
must be controlled or. T is is achieved by concomitantly
5 32 measuring one o the ubiquitously expressed housekeeping
10 1,024 genes, or example, ABL1, BCR.
20 >1,000,000
Consensus Prim er PCR and Allele-Speci c
*The number of copies of a speci c DNA sequence doubles with each Oligonucleotide PCR
ampli cation. PCR usually consists of a series of 20 to 40 repeated
temperature changes called cycles; each cycle typically consists of two Consensus primer PCR and allele-speci c oligonucleotide
to three discrete temperature steps. Most commonly, PCR is carried out PCR (ASO-PCR) are the two Ig PCR strategies or MRD
with cycles that have three temperature steps. The temperatures used studies. ASO-PCR utilizes primers designed to anneal to a
and the length of time they are applied in each cycle depend on a vari- unique patient-speci c Ig sequence and subsequently is used
ety of parameters. These include the enzyme used for DNA synthesis, the
concentration of divalent ions and dNTPs in the reaction, and the melting to monitor sequential samples in ollow-up studies. T is
−4
−2
temperature (Tm) of the primers. PCR may reach a plateau with no more qualitative method has a sensitivity o 1 × 10 to 1 × 10 .
copies produced because of reagent limitations, inhibitors, etc. ASO-PCR signi cantly improves the sensitivity o MRD
studies, but ASO-PCR is time consuming and expensive.
Combination o ASO primers and consensus oligonucle-
otide probes make it accessible to Q-PCR, permitting pre-
o the DNA surrounding the sequence o interest is ampli- −4
ed. T is is ollowed by a second round o ampli cation to cise quanti cation o MRD with a sensitivity o 1 × 10 to
−5
ampli y the speci c gene sequence to be studied. Another 1 × 10 .
recent modi cation o the PCR technique has been used suc-
cess ully to di erentiate alleles o the same gene. Other Ampli cation Methods
PCR is not the only method o ampli cation. ranscription-
Real-Tim e PCR
mediated ampli cation or ribosomal RNA and strand dis-
Another method based on PCR is real-time PCR (R -PCR). placement that uses primers to bind on the same side as the
However, this method is not used as much now as in the DNA target can be used.
past. R -PCR detects RNA rom viable cells and thus tar- A method that is making its way rom the research labo-
gets genes expressed that are likely to have unctional role, ratory to becoming a mainstream technique is loop-mediated
directly or indirectly, in cellular proli eration. T e appli- isothermal ampli cation (LAMP). T is technique di ers rom
cation o this technique is in the quantitation o speci c traditional PCR because it starts with our primers, not the
DNA sequences o interest and or identi cation o point two used by PCR. wo o the our primers each have a sec-
mutations. tion, which is complementary to one end o a target DNA
T is PCR variation uses f uorescence resonance energy sequence but each also has an intentionally “mirrored” sec-
trans er (FRE ). T is PCR variation is particularly appealing tion o the target. T is allows each primer to have the capa-
because the procedure is less susceptible to amplicon con- bility o orming a hairpin structure. T e hairpin primers
tamination and is more accurate in quanti ying the initial delineate the region to be detected through its ampli cation,
copy number. i it is present in the specimen. T e two other primers act
as primer initiating points which cause f ipping o the intact
Quantitative PCR (Q-PCR)
double-stranded ends to hairpins needed to continue the
Q-PCR assumes 100% e ciency, but there is variation in the replications.
e ciency o ampli cation. In very small specimens, there Selection o primers is more challenging with LAMP than
may be no ampli cation. traditional PCR. Currently, this method is being to be or
Quanti cation o speci c sequences o DNA has been in ectious disease detection, but urther applications could
greatly simpli ed by real-time quantitative polymerase emerge.
chain reaction (RQ-PCR or Q-PCR). In Q-PCR, the rate o
accumulation o amplicons is proportional to the number o Analysis of Ampli cation Products
target transcripts in the starting material during the expo-
nential phase o the PCR. T is technique also o ers increased Detection o DNA products by PCR assay can be convention-
speci city with the inclusion o the third reporter labeled ally analyzed using agarose gel electrophoresis a er ethidium
oligonucleotide probe using hydrolysis-based technology, bromide staining. T is technique is simply an extra step a er a