Page 676 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 676
660 PART 8 ■ Fundamentals of Hematological Analysis
Tere are two di erent pyrosequencing strategies that
BOX 31.3 are currently available: solid-phase pyrosequencing and
liquid-phase pyrosequencing. Solid-phase pyrosequencing
utilizes immobilized DNA in a three-enzyme system. In this
Limitations of DNA Sequencing system, a washing step is per ormed to remove the excess
■ Large amounts o normal tissue required substrate a er each nucleotide addition. Using this method,
■ Sensitivity—tumor mixed with normal cells the DNA to be sequenced is broken up into ragments o
■ Heterozygosity—most mutation, hal o DNA is ~100 base pairs and denatured to orm single-stranded DNA
normal (ssDNA). T en single ssDNA amplicons are immobilized
onto microscopic beads and placed into separate wells. In liq-
From Heriot K. Welcome to the beginning: molecular pathology or the uid-phase pyrosequencing, a nucleotide-degrading enzyme
community hospital pathologist and medical technologist, ASCP Annual is introduced to make a our-enzyme system. Addition o
Meeting, ampa, FL, 2014. this enzyme has eliminated the need or solid support and
intermediate washing and enables the pyrosequencing reac-
tion to be per ormed in a single tube.
2. T e second step involves adding primers to the ssDNA.
Primers are short synthetic segments o ssDNA that con- Southern Blot Technique
tain a nucleotide sequence complementary to a short T e Southern and Northern blot techniques are historic
strand o target DNA. T e patient’s DNA serves as a techniques used to detect DNA and RNA, respectively. T e
template to copy. DNA polymerase catalyzes the addition Southern blot procedure (Figs. 31.9 and 31.10) can be used
o the appropriate nucleotides to the preexisting primer. in clinical laboratories, but the Northern blot technique is
DNA synthesis is terminated when the deoxynucleotide is used in research setting.
incorporated into a growing DNA chain. Specimen DNA is denatured and treated with restric-
tion enzymes to create DNA ragments; then, the ssDNA
Pyrosequencing ragments are separated by electrophoresis (Fig. 14.7). T e
In attempt to nd a aster and less expensive way o molecu- electrophoretically separated ragments are then blotted to
lar sequencing, pyrosequencing has emerged as a method. a nitrocellulose membrane, retaining their electrophoretic
Pyrosequencing is a DNA sequencing technique that is based position and hybridized with radiolabeled single-stranded
on the detection o released pyrophosphate (PPi) during DNA ragments with sequences complementary to those
DNA synthesis. In a cascade o enzymatic reactions, visible being sought. T e resulting dsDNA bearing the radiolabel, i
light is generated that is proportional to the number o incor- present, is then detected by radiography.
porated nucleotides. T e Southern blot procedure has clinical diagnostic appli-
Te cascade starts with a nucleic acid polymerization cations or disorders associated with signi cant changes in
reaction in which inorganic PPi is released as a result o DNA, a deletion or insertion o at least 50 to 100 bp (e.g.,
nucleotide incorporation by polymerase. T e released PPi is ragile X syndrome), and determination o clonality in
subsequently converted to A P by A P sul urylase, which lymphomas o or B cell origin. I a single-base mutation
provides the energy to luci erase to oxidize luci erin and changes an enzyme restriction site on the DNA, resulting in
generate light. Because the added nucleotide is known, the an altered band or ragment size, the Southern blot proce-
sequence o the template can be determined. dure can detect these changes in DNA sequences.
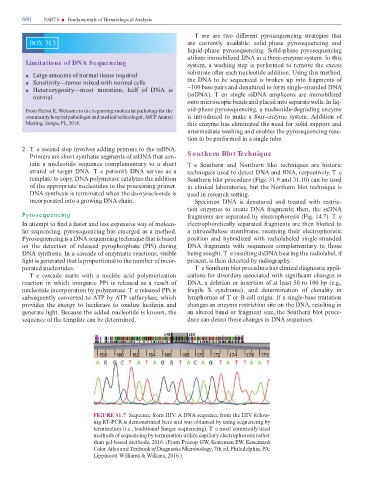
FIGURE 31.7 Sequence rom HIV. A DNA sequence rom the HIV ollow-
ing R -PCR is demonstrated here and was obtained by using sequencing by
termination (i.e., traditional Sanger sequencing). T e most commonly used
methods o sequencing by termination utilize capillary electrophoresis rather
than gel-based methods, 2016. (From Procop GW, Koneman EW. Koneman’s
Color Atlas and extbook o Diagnostic Microbiology, 7th ed, Philadelphia, PA:
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2016.).