Page 110 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 110
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch04_085-114.indd Page 87 9/1/10 9:37 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch04_085-114.indd Page 87 9/1/10 9:37 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
smallest particle of a compound or a gaseous element that
can exist and still retain the characteristic properties of that
substance.
MOLECULES INTERACT
Some molecules of solids and liquids interact, strongly
attracting and clinging to one another. When this attractive
force is between the same kind of molecules, it is called cohe-
sion. It is a stronger cohesion that makes solids and liquids
different from gases, and without cohesion, all matter would
be in the form of gases. Sometimes one kind of molecule
attracts and clings to a different kind of molecule. Th e attrac-
tive force between unlike molecules is called adhesion. Water
wets your skin because the adhesion of water molecules and
skin is stronger than the cohesion of water molecules. Some
substances, such as glue, have a strong force of adhesion when
they harden from a liquid state, and they are called adhesives.
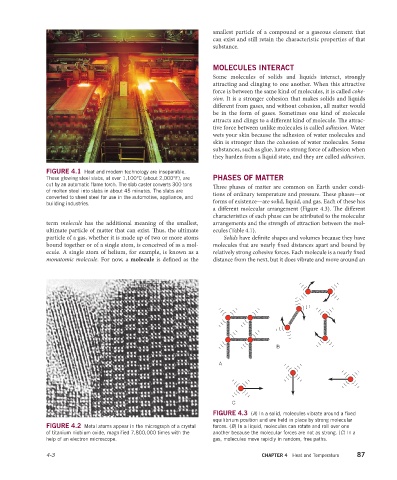
FIGURE 4.1 Heat and modern technology are inseparable.
These glowing steel slabs, at over 1,100°C (about 2,000°F), are PHASES OF MATTER
cut by an automatic flame torch. The slab caster converts 300 tons Three phases of matter are common on Earth under condi-
of molten steel into slabs in about 45 minutes. The slabs are
converted to sheet steel for use in the automotive, appliance, and tions of ordinary temperature and pressure. Th ese phases—or
building industries. forms of existence—are solid, liquid, and gas. Each of these has
a different molecular arrangement (Figure 4.3). Th e diff erent
characteristics of each phase can be attributed to the molecular
term molecule has the additional meaning of the smallest, arrangements and the strength of attraction between the mol-
ultimate particle of matter that can exist. Thus, the ultimate ecules (Table 4.1).
particle of a gas, whether it is made up of two or more atoms Solids have defi nite shapes and volumes because they have
bound together or of a single atom, is conceived of as a mol- molecules that are nearly fixed distances apart and bound by
ecule. A single atom of helium, for example, is known as a relatively strong cohesive forces. Each molecule is a nearly fi xed
monatomic molecule. For now, a molecule is defined as the distance from the next, but it does vibrate and move around an
B
A
C
FIGURE 4.3 (A) In a solid, molecules vibrate around a fixed
equilibrium position and are held in place by strong molecular
FIGURE 4.2 Metal atoms appear in the micrograph of a crystal forces. (B) In a liquid, molecules can rotate and roll over one
of titanium niobium oxide, magnified 7,800,000 times with the another because the molecular forces are not as strong. (C) In a
help of an electron microscope. gas, molecules move rapidly in random, free paths.
4-3 CHAPTER 4 Heat and Temperature 87