Page 522 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 522
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch19_477-500.indd Page 499 9/3/10 6:23 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch19_477-500.indd Page 499 9/3/10 6:23 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
Group A—Continued Group B—Continued
7. Compare the energy released by a small atomic bomb blast 7. Compare the energy released by a strong earthquake in a
(magnitude 4.0) to an earthquake of 9.1 magnitude. tectonically inactive northeastern state (magnitude 5.2) to the
1964 Prince William Sound, Alaska, earthquake along a
subduction zone.
8. Compare the ground motion associated with an earthquake that 8. Compare the ground motion (surface wave amplitude)
is felt but creates no damage (magnitude 3.5) to a strong associated with a strong earthquake in a tectonically inactive
earthquake with destruction (6.5 magnitude). northeastern state (magnitude 5.2) to the 1964 Prince William
Sound, Alaska, earthquake.
9. An earthquake occurred at 6:05 :00 a.m. and seismographs in the 9. An earthquake occurred at 12:35:40 p.m. and seismographs in the
region of the earthquake detected the P- and S-wave arrivals at region of the earthquake detected the P- and S-wave arrivals at
the times noted in the following table: the times noted in the following table:
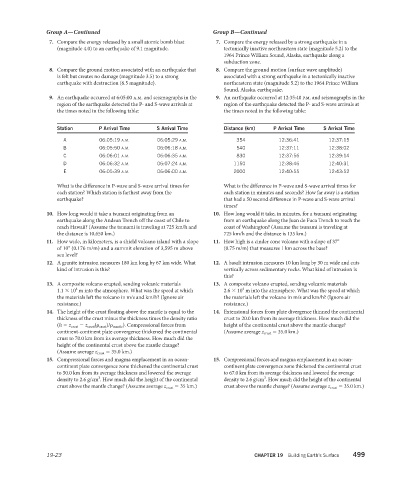
Station P Arrival Time S Arrival Time Distance (km) P Arrival Time S Arrival Time
A 06:05:19 A.M. 06:05:29 A.M. 354 12:36:41 12:37:15
B 06:05:50 A.M. 06:06:18 A.M. 540 12:37:11 12:38:02
C 06:06:01 A.M. 06:06:35 A.M. 830 12:37:56 12:39:14
D 06:06:32 A.M. 06:07:24 A.M. 1150 12:38:46 12:40:31
E 06:05:39 A.M. 06:06:00 A.M. 2000 12:40:55 12:43:52
What is the difference in P-wave and S-wave arrival times for What is the difference in P-wave and S-wave arrival times for
each station? Which station is farthest away from the each station in minutes and seconds? How far away is a station
earthquake? that had a 50 second difference in P-wave and S-wave arrival
times?
10. How long would it take a tsunami originating from an 10. How long would it take, in minutes, for a tsunami originating
earthquake along the Andean Trench off the coast of Chile to from an earthquake along the Juan de Fuca Trench to reach the
reach Hawaii? (Assume the tsunami is traveling at 725 km/h and coast of Washington? (Assume the tsunami is traveling at
the distance is 10,650 km.) 725 km/h and the distance is 135 km.)
11. How wide, in kilometers, is a shield volcano island with a slope 11. How high is a cinder cone volcano with a slope of 37°
of 10° (0.176 m/m) and a summit elevation of 3,595 m above (0.75 m/m) that measures 1 km across the base?
sea level?
12. A granite intrusion measures 180 km long by 67 km wide. What 12. A basalt intrusion measures 10 km long by 30 m wide and cuts
kind of intrusion is this? vertically across sedimentary rocks. What kind of intrusion is
this?
13. A composite volcano erupted, sending volcanic materials 13. A composite volcano erupted, sending volcanic materials
4
4
1.1 × 10 m into the atmosphere. What was the speed at which 2.6 × 10 m into the atmosphere. What was the speed at which
the materials left the volcano in m/s and km/h? (Ignore air the materials left the volcano in m/s and km/h? (Ignore air
resistance.) resistance.)
14. The height of the crust floating above the mantle is equal to the 14. Extensional forces from plate divergence thinned the continental
thickness of the crust minus the thickness times the density ratio crust to 20.0 km from its average thickness. How much did the
(h = z crust − z crust (ρ crust )/ρ mantle ). Compressional forces from height of the continental crust above the mantle change?
continent-continent plate convergence thickened the continental (Assume average z crust = 35.0 km.)
crust to 70.0 km from its average thickness. How much did the
height of the continental crust above the mantle change?
(Assume average z crust = 35.0 km.)
15. Compressional forces and magma emplacement in an ocean- 15. Compressional forces and magma emplacement in an ocean-
continent plate convergence zone thickened the continental crust continent plate convergence zone thickened the continental crust
to 50.0 km from its average thickness and lowered the average to 67.0 km from its average thickness and lowered the average
3
3
density to 2.6 g/cm . How much did the height of the continental density to 2.6 g/cm . How much did the height of the continental
crust above the mantle change? (Assume average z crust = 35 km.) crust above the mantle change? (Assume average z crust = 35.0 km.)
19-23 CHAPTER 19 Building Earth’s Surface 499