Page 16 - Focus SPM KSSM Tg 4.5 - Add Maths
P. 16
Additional Mathematics SPM Chapter 2 Quadratic Functions
(e) 2x(4x – 3) = 5 (f) 7x = 5x + 3 5. Given the quadratic equation mx – 5nx + m = 0
2
2
(g) 2(5x – 9) = 3x (h) (x + 2)(3x + 1) = x – 1 has two equal roots. Find the relation between m
2
and n.
2. Find the range of values of p if each of the following
2
quadratic equations has two different real roots. 6. Given the quadratic equation p(x + 4) = 8qx has two
(a) x – 6x + 4p = 0 (b) 2px + 5(x – 1) = 0 equal roots. Find the ratio of p : q. Hence, find the
2
2
(c) x(3x + 7) = – 6 – p (d) x(9x + 1) = p(6x – p) roots.
7. If the ratio of h : k = 3 : 2, determine the types of
3. Find the value of k if each of the following quadratic roots of the quadratic equation 9kx + k = 4hx.
2
equations has two equal real roots.
(a) 3x – 2kx + k = 0 8. Given that 5 and – 4 are the roots of the quadratic
2
(b) kx – 4x + 3k = 4 equation px – 2x + q = 0. Find
2
2
(c) 4kx = x(3k – x) – 1 (a) the value of p and the value of q,
2
(d) x(4x – k) = k – 2(x + 1) (b) the value of m where the quadratic equation
px – 2x + q = m has two equal roots. Form 4
2
4. Find the range of values of h if each of the following
quadratic equations has no roots.
(a) x – 2x + 5h = 0 (b) x + 2hx + (2 – h) = 0
2
2
2
(c) 5 – 2x = (3 – h)x (d) 4x – 4hx + h = 5x
2
2
2
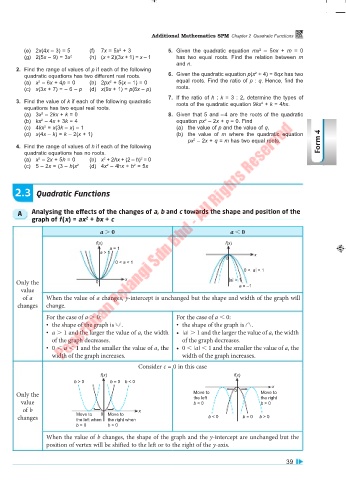
2.3 Quadratic Functions
A Analysing the effects of the changes of a, b and c towards the shape and position of the
graph of f(x) = ax + bx + c
2
a . 0 a 0
f(x) f(x)
a = 1
a > 1 x
0
0 < a < 1
0 < a < 1
x a > 1
Only the 0 a = –1
value
of a When the value of a changes, y-intercept is unchanged but the shape and width of the graph will
changes change.
For the case of a . 0: For the case of a 0:
• the shape of the graph is . • the shape of the graph is .
• a . 1 and the larger the value of a, the width • a . 1 and the larger the value of a, the width
of the graph decreases. of the graph decreases.
• 0 a 1 and the smaller the value of a, the • 0 a 1 and the smaller the value of a, the
width of the graph increases. width of the graph increases.
Consider c = 0 in this case
f(x) f(x)
b > 0 b = 0 b < 0
x
Only the Move to 0 Move to
the left
the right
value b < 0 b > 0
of b x
changes Move to 0 Move to b < 0 b = 0 b > 0
the right when
the left when
b > 0 b < 0
When the value of b changes, the shape of the graph and the y-intercept are unchanged but the
position of vertex will be shifted to the left or to the right of the y-axis.
39