Page 18 - Focus SPM KSSM Tg 4.5 - Add Maths
P. 18
Additional Mathematics SPM Chapter 2 Quadratic Functions
2
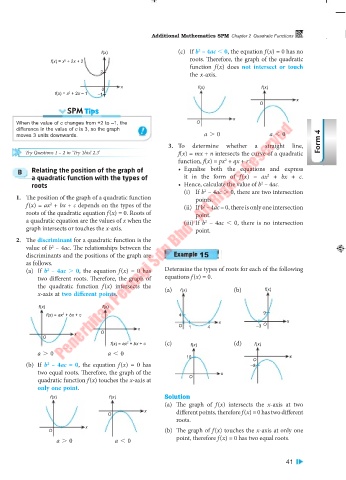
f(x) (c) If b – 4ac 0, the equation f (x) = 0 has no
roots. Therefore, the graph of the quadratic
f(x) = x + 2x + 2
2
function f (x) does not intersect or touch
2 the x-axis.
x f(x) f(x)
0
f(x) = x + 2x – 1 –1
2
x
O
SPM Tips
x
When the value of c changes from +2 to –1, the O
difference in the value of c is 3, so the graph
moves 3 units downwards. a . 0 a 0
3. To determine whether a straight line, Form 4
Try Questions 1 – 2 in ‘Try This! 2.3’ f(x) = mx + n intersects the curve of a quadratic
2
function, f(x) = px + qx + r :
B Relating the position of the graph of • Equalise both the equations and express
2
a quadratic function with the types of it in the form of f (x) = ax + bx + c.
2
roots • Hence, calculate the value of b – 4ac.
(i) If b – 4ac . 0, there are two intersection
2
1. The position of the graph of a quadratic function points.
f (x) = ax + bx + c depends on the types of the (ii) If b – 4ac = 0, there is only one intersection
2
2
roots of the quadratic equation f (x) = 0. Roots of point.
a quadratic equation are the values of x when the (iii) If b – 4ac 0, there is no intersection
2
graph intersects or touches the x-axis. point.
2. The discriminant for a quadratic function is the
value of b – 4ac. The relationships between the
2
discriminants and the positions of the graph are 15
as follows.
(a) If b – 4ac . 0, the equation f (x) = 0 has Determine the types of roots for each of the following
2
two different roots. Therefore, the graph of equations f (x) = 0.
the quadratic function f (x) intersects the (a) (b) f(x)
x-axis at two different points. f(x)
f(x) f(x)
2
f(x) = ax + bx + c 4 9
x x
O 1 4 –3 O
x
x O
O
2
f(x) = ax + bx + c (c) f(x) (d) f(x)
a . 0 a 0
10 O x
2
(b) If b – 4ac = 0, the equation f (x) = 0 has –8
two equal roots. Therefore, the graph of the x
quadratic function f (x) touches the x-axis at O
only one point.
f(x) f(x) Solution
(a) The graph of f (x) intersects the x-axis at two
x different points, therefore f (x) = 0 has two different
O
roots.
x
O (b) The graph of f (x) touches the x-axis at only one
a . 0 a 0 point, therefore f (x) = 0 has two equal roots.
41