Page 493 - MARSIUM'21 COMP OF PAPER
P. 493
Muhammad Amirul Asraf Bin Sungip (2022)
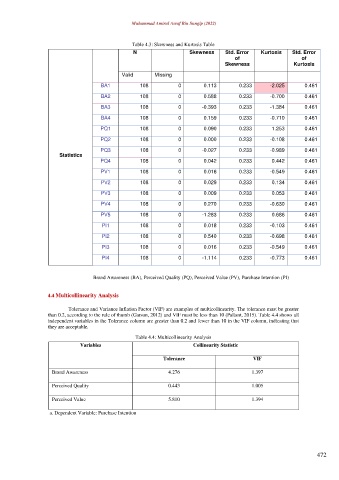
Table 4.3: Skewness and Kurtosis Table
N Skewness Std. Error Kurtosis Std. Error
of of
Skewness Kurtosis
Valid Missing
BA1 108 0 0.113 0.233 -2.025 0.461
BA2 108 0 0.588 0.233 -0.700 0.461
BA3 108 0 -0.393 0.233 -1.384 0.461
BA4 108 0 0.159 0.233 -0.710 0.461
PQ1 108 0 0.090 0.233 1.253 0.461
PQ2 108 0 0.000 0.233 -0.108 0.461
PQ3 108 0 -0.027 0.233 -0.989 0.461
Statistics
PQ4 108 0 0.042 0.233 0.442 0.461
PV1 108 0 0.016 0.233 -0.549 0.461
PV2 108 0 0.029 0.233 0.134 0.461
PV3 108 0 0.009 0.233 0.053 0.461
PV4 108 0 0.270 0.233 -0.630 0.461
PV5 108 0 -1.283 0.233 0.686 0.461
PI1 108 0 0.018 0.233 -0.103 0.461
PI2 108 0 0.540 0.233 -0.698 0.461
PI3 108 0 0.016 0.233 -0.549 0.461
PI4 108 0 -1.114 0.233 -0.773 0.461
Brand Awareness (BA), Perceived Quality (PQ), Perceived Value (PV), Purchase Intention (PI)
4.4 Multicollinearity Analysis
Tolerance and Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) are examples of multicollinearity. The tolerance must be greater
than 0.2, according to the rule of thumb (Garson, 2012) and VIF must be less than 10 (Pallant, 2015). Table 4.4 shows all
independent variables in the Tolerance column are greater than 0.2 and fewer than 10 in the VIF column, indicating that
they are acceptable.
Table 4.4: Multicollinearity Analysis
Variables Collinearity Statistic
Tolerance VIF
Brand Awareness 4.276 1.397
Perceived Quality 0.443 1.005
Perceived Value 5.810 1.394
a. Dependent Variable: Purchase Intention
472