Page 419 - alligood 8th edition_Neat
P. 419
400 UNIT IV Nursing Theories
MAJOR CONCEPTS & DEFINITIONS—cont’d
Commitment to a Plan of Action exert relatively high control, such as choice of ice
This commitment describes the concept of intention cream or an apple for a snack.
and identification of a planned strategy that leads to
implementation of health behavior. Health-Promoting Behavior
A health-promoting behavior is an end point or
Immediate Competing Demands action outcome that is directed toward attaining
and Preferences positive health outcomes such as optimal well-
Competing demands are alternative behaviors over being, personal fulfillment, and productive living.
which individuals have low control, because there Examples of health-promoting behavior are eating a
are environmental contingencies such as work or healthy diet, exercising regularly, managing stress,
family care responsibilities. Competing preferences gaining adequate rest and spiritual growth, and
are alternative behaviors over which individuals building positive relationships.
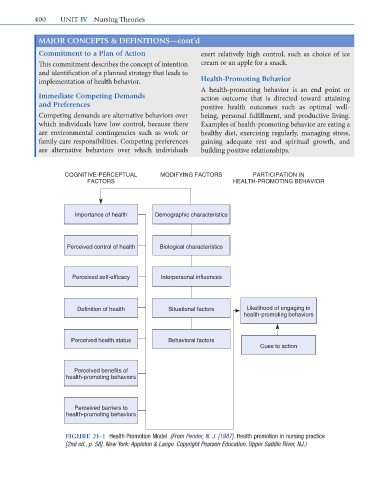
COGNITIVE-PERCEPTUAL MODIFYING FACTORS PARTICIPATION IN
FACTORS HEALTH-PROMOTING BEHAVIOR
Importance of health Demographic characteristics
Perceived control of health Biological characteristics
Perceived self-efficacy Interpersonal influences
Definition of health Situational factors Likelihood of engaging in
health-promoting behaviors
Perceived health status Behavioral factors
Cues to action
Perceived benefits of
health-promoting behaviors
Perceived barriers to
health-promoting behaviors
FIGURE 21-1 Health Promotion Model. (From Pender, N. J. [1987]. Health promotion in nursing practice
[2nd ed., p. 58]. New York: Appleton & Lange. Copyright Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ.)