Page 421 - alligood 8th edition_Neat
P. 421
402 UNIT IV Nursing Theories
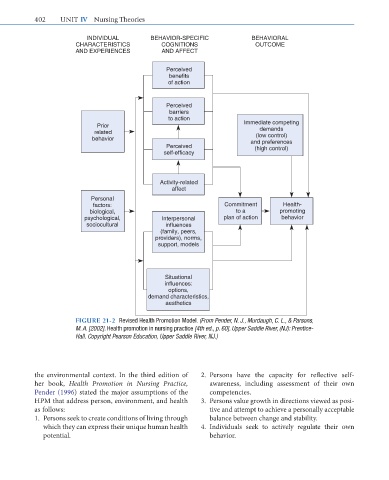
INDIVIDUAL BEHAVIOR-SPECIFIC BEHAVIORAL
CHARACTERISTICS COGNITIONS OUTCOME
AND EXPERIENCES AND AFFECT
Perceived
benefits
of action
Perceived
barriers
to action
Prior Immediate competing
demands
related (low control)
behavior and preferences
Perceived (high control)
self-efficacy
Activity-related
affect
Personal
factors: Commitment Health-
biological, to a promoting
psychological, Interpersonal plan of action behavior
sociocultural influences
(family, peers,
providers), norms,
support, models
Situational
influences:
options,
demand characteristics,
aesthetics
FIGURE 21-2 Revised Health Promotion Model. (From Pender, N. J., Murdaugh, C. L., & Parsons,
M. A. [2002]. Health promotion in nursing practice [4th ed., p. 60]. Upper Saddle River, (NJ): Prentice-
Hall. Copyright Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ.)
the environmental context. In the third edition of 2. Persons have the capacity for reflective self-
her book, Health Promotion in Nursing Practice, awareness, including assessment of their own
Pender (1996) stated the major assumptions of the competencies.
HPM that address person, environment, and health 3. Persons value growth in directions viewed as posi-
as follows: tive and attempt to achieve a personally acceptable
1. Persons seek to create conditions of living through balance between change and stability.
which they can express their unique human health 4. Individuals seek to actively regulate their own
potential. behavior.