Page 521 - alligood 8th edition_Neat
P. 521
502 UNIT IV Nursing Theories
MAJOR CONCEPTS & DEFINITIONS—cont’d
Mind-Body Relationships or her effectiveness or fulfillment (given circum-
We are all biophysical, psychosocial beings who stances), or promote his or her growth (Erickson,
want to develop our potential, that is, to be the best Tomlin, & Swain, 2002, p. 48).
we can be (Erickson, Tomlin, & Swain, 2002, p. 70). n Self-Care Resources
Self-care resources are “the internal resources, as
Self-Care well as additional resources, mobilized through self-
Self-care involves the use of knowledge, resources, care action that help gain, maintain, and promote an
and actions, as follows: optimum level of holistic health” (Erickson, Tomlin,
n Self-Care Knowledge & Swain, 2002, pp. 254–255).
At some level, a person knows what has made n Self-Care Action
him or her sick, lessened his or her effectiveness, or Self-care action is “the development and utiliza-
interfered with his or her growth. The person also tion of self-care knowledge and self-care resources”
knows what will make him or her well, optimize his (Erickson, Tomlin, & Swain, 2002, p. 254).
Use of Empirical Evidence
Several studies provided initial evidence for philo-
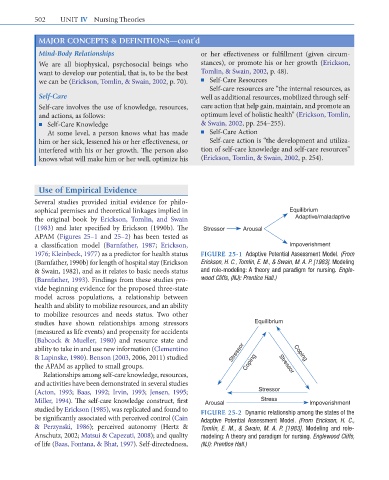
sophical premises and theoretical linkages implied in Equilibrium
the original book by Erickson, Tomlin, and Swain Adaptive/maladaptive
(1983) and later specified by Erickson (1990b). The Stressor Arousal
APAM (Figures 25–1 and 25–2) has been tested as
a classification model (Barnfather, 1987; Erickson, Impoverishment
1976; Kleinbeck, 1977) as a predictor for health status FIGURE 25-1 Adaptive Potential Assessment Model. (From
(Barnfather, 1990b) for length of hospital stay (Erickson Erickson, H. C., Tomlin, E. M., & Swain, M. A. P. [1983]. Modeling
& Swain, 1982), and as it relates to basic needs status and role-modeling: A theory and paradigm for nursing. Engle-
(Barnfather, 1993). Findings from these studies pro- wood Cliffs, (NJ): Prentice Hall.)
vide beginning evidence for the proposed three-state
model across populations, a relationship between
health and ability to mobilize resources, and an ability
to mobilize resources and needs status. Two other
studies have shown relationships among stressors Equilibrium
(measured as life events) and propensity for accidents
(Babcock & Mueller, 1980) and resource state and
ability to take in and use new information (Clementino Stressor
& Lapinske, 1980). Benson (2003, 2006, 2011) studied Coping
the APAM as applied to small groups. Coping Stressor
Relationships among self-care knowledge, resources,
and activities have been demonstrated in several studies
(Acton, 1993; Baas, 1992; Irvin, 1993; Jensen, 1995; Stressor
Miller, 1994). The self-care knowledge construct, first Arousal Stress Impoverishment
studied by Erickson (1985), was replicated and found to FIGURE 25-2 Dynamic relationship among the states of the
be significantly associated with perceived control (Cain Adaptive Potential Assessment Model. (From Erickson, H. C.,
& Perzynski, 1986); perceived autonomy (Hertz & Tomlin, E. M., & Swain, M. A. P. [1983]. Modeling and role-
Anschutz, 2002; Matsui & Capezuti, 2008); and quality modeling: A theory and paradigm for nursing. Englewood Cliffs,
of life (Baas, Fontana, & Bhat, 1997). Self-directedness, (NJ): Prentice Hall.)