Page 11 - MGPI_Case_Study
P. 11
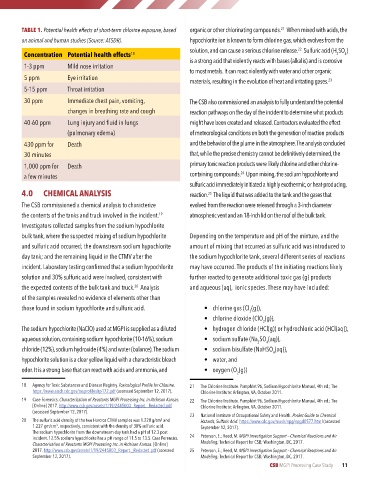
TABLE 1. Potential health effects of short-term chlorine exposure, based organic or other chlorinating compounds. When mixed with acids, the
21
on animal and human studies (Source: ATSDR). hypochlorite ion is known to form chlorine gas, which evolves from the
18
22
Concentration Potential health effects 18 solution, and can cause a serious chlorine release. Sulfuric acid (H SO )
2
4
is a strong acid that violently reacts with bases (alkalis) and is corrosive
1-3 ppm Mild nose irritation
to most metals. It can react violently with water and other organic
5 ppm Eye irritation
23
materials, resulting in the evolution of heat and irritating gases.
5-15 ppm Throat irritation
30 ppm Immediate chest pain, vomiting, The CSB also commissioned an analysis to fully understand the potential
changes in breathing rate and cough reaction pathways on the day of the incident to determine what products
40-60 ppm Lung injury and fluid in lungs might have been created and released. Contractors evaluated the effect
(pulmonary edema) of meteorological conditions on both the generation of reaction products
430 ppm for Death and the behavior of the plume in the atmosphere. The analysis concluded
30 minutes that, while the precise chemistry cannot be definitively determined, the
1,000 ppm for Death primary toxic reaction products were likely chlorine and other chlorine-
24
a few minutes containing compounds. Upon mixing, the sodium hypochlorite and
sulfuric acid immediately initiated a highly exothermic, or heat-producing,
4.0 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS reaction. The liquid that was added to the tank and the gases that
25
The CSB commissioned a chemical analysis to characterize evolved from the reaction were released through a 3-inch diameter
19
the contents of the tanks and truck involved in the incident. atmospheric vent and an 18-inch lid on the roof of the bulk tank.
Investigators collected samples from the sodium hypochlorite
bulk tank, where the suspected mixing of sodium hypochlorite Depending on the temperature and pH of the mixture, and the
and sulfuric acid occurred; the downstream sodium hypochlorite amount of mixing that occurred as sulfuric acid was introduced to
day tank; and the remaining liquid in the CTMV after the the sodium hypochlorite tank, several different series of reactions
incident. Laboratory testing confirmed that a sodium hypochlorite may have occurred. The products of the initiating reactions likely
solution and 30% sulfuric acid were involved, consistent with further reacted to generate additional toxic gas (g) products
the expected contents of the bulk tank and truck. Analysis and aqueous (aq), ionic species. These may have included:
20
of the samples revealed no evidence of elements other than
those found in sodium hypochlorite and sulfuric acid. • chlorine gas (Cl (g)),
2
• chlorine dioxide (ClO (g)),
2
The sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) used at MGPI is supplied as a diluted • hydrogen chloride (HCl(g)) or hydrochloric acid (HCl(aq)),
aqueous solution, containing sodium hypochlorite (10-16%), sodium • sodium sulfate (Na SO (aq)),
2 4
chloride (12%), sodium hydroxide (4%) and water (balance). The sodium • sodium bisulfate (NaHSO (aq)),
4
hypochlorite solution is a clear yellow liquid with a characteristic bleach • water, and
odor. It is a strong base that can react with acids and ammonia, and • oxygen (O (g))
2
18 Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological Profile for Chlorine. 21 The Chlorine Institute. Pamphlet 96, Sodium Hypochlorite Manual, 4th ed.; The
https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp172.pdf (accessed September 12, 2017). Chlorine Institute: Arlington, VA, October 2011.
19 Case Forensics. Characterization of Reactants MGPI Processing Inc. in Atchison Kansas. 22 The Chlorine Institute. Pamphlet 96, Sodium Hypochlorite Manual, 4th ed.; The
[Online] 2017. http://www.csb.gov/assets/1/19/2445003_Report._Redacted.pdf Chlorine Institute: Arlington, VA, October 2011.
(accessed September 12, 2017).
23 National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health. Pocket Guide to Chemical
20 The sulfuric acid density of the two Harcros CTMV samples was 1.228 g/cm and Hazards, Sulfuric Acid. https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0577.html (accessed
3
3
1.227 gm/cm , respectively, consistent with the density of 30% sulfuric acid. September 12, 2017).
The sodium hypochlorite from the downstream day tank had a pH of 12.3 post Peterson, E.; Reed, M. MGPI Investigation Support – Chemical Reactions and Air
incident. 12.5% sodium hypochlorite has a pH range of 11.5 to 13.5. Case Forensics. 24
Characterization of Reactants MGPI Processing Inc. in Atchison Kansas. [Online] Modeling; Technical Report for CSB; Washington, DC, 2017.
2017. http://www.csb.gov/assets/1/19/2445003_Report._Redacted.pdf (accessed 25 Peterson, E.; Reed, M. MGPI Investigation Support – Chemical Reactions and Air
September 12, 2017). Modeling; Technical Report for CSB; Washington, DC, 2017.
CSB MGPI Processing Case Study 11