Page 182 - Class-11-Physics-Part-1_Neat
P. 182
168 PHYSICS
there is no need to treat angular velocity as a
u Example 7.13 Obtain Eq. (7.38) from first
vector. Further, the angular acceleration, α =
principles.
dω/dt.
The kinematical quantities in rotational Answer The angular acceleration is uniform,
motion, angular displacement (θ), angular hence
velocity (ω) and angular acceleration (α)
respectively are analogous to kinematic dω = α = constant (i)
quantities in linear motion, displacement (x), dt
velocity (v) and acceleration (a). We know the Integrating this equation,
kinematical equations of linear motion with
uniform (i.e. constant) acceleration: ω = ∫ α dt + c
v = v + at (a)
α
=
t
0 α + c (as is constant)
1
x = x + υ t + at 2 (b) At t = 0, ω = ω (given)
0
0
0
2 From (i) we get at t = 0, ω = c = ω
0
2
2
υ = υ + 2ax (c) Thus, ω = αt + ω as required.
0
0 With the definition of ω = dθ/dt we may
where x = initial displacement and v = initial
0 0 integrate Eq. (7.38) to get Eq. (7.39). This
velocity. The word ‘initial’ refers to values of the derivation and the derivation of Eq. (7.40) is
quantities at t = 0 left as an exercise.
The corresponding kinematic equations for
rotational motion with uniform angular
acceleration are: u Example 7.14 The angular speed of a
motor wheel is increased from 1200 rpm
ω = ω + t α (7.38)
0 to 3120 rpm in 16 seconds. (i) What is its
1 angular acceleration, assuming the
θ = θ + ω t + α t 2 (7.39) acceleration to be uniform? (ii) How many
0
0
2
revolutions does the engine make during
andω 2 = ω 2 + 2 ( –θ ) (7.40) this time?
θ
α
0 0
where θ = initial angular displacement of the Answer
0
rotating body, and ω = initial angular velocity
0 (i) We shall use ω = ω + αt
0
of the body.
ω = initial angular speed in rad/s
0
= 2π × angular speed in rev/s
2π × angular speed in rev/min
=
60 s/min
2π × 1200
= rad/s
60
= 40π rad/s
Similarly ω = final angular speed in rad/s
2π × 3120
= rad/s
60
= 2π × 52 rad/s
= 104 π rad/s
∴ Angular acceleration
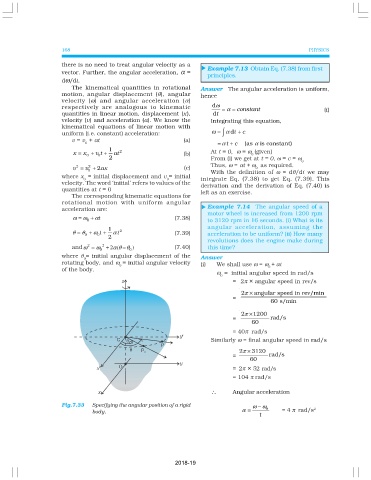
Fig.7.33 Specifying the angular position of a rigid ω ω 0
−
body. α = = 4 π rad/s 2
t
2018-19