Page 291 - Robot Design Handbook ROBOCON Malaysia 2019
P. 291
5.0 PROJECT CONCEPT ANALYSIS
5.1 Analysis of Selection of DC Motors and Servo Motors
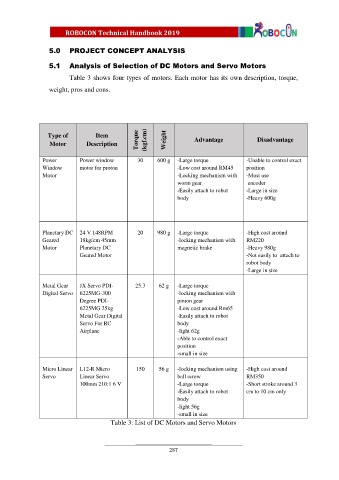
Table 3 shows four types of motors. Each motor has its own description, torque,
weight, pros and cons.
Type of Item
Motor Description Torque (kgf.cm) Weight Advantage Disadvantage
Power Power window 30 600 g -Large torque -Unable to control exact
Window motor for proton -Low cost around RM45 position
Motor -Locking mechanism with -Must use
worm gear encoder
-Easily attach to robot -Large in size
body -Heavy 600g
Planetary DC 24 V 148RPM 20 980 g -Large torque -High cost around
Geared 18kgfcm 45mm -locking mechanism with RM220
Motor Planetary DC magnetic brake -Heavy 980g
Geared Motor -Not easily to attach to
robot body
-Large in size
Metal Gear JX Servo PDI- 25.3 62 g -Large torque
Digital Servo 6225MG-300 -locking mechanism with
Degree PDI- pinion gear
6225MG 25kg -Low cost around Rm65
Metal Gear Digital -Easily attach to robot
Servo For RC body
Airplane -light 62g
-Able to control exact
position
-small in size
Micro Linear L12-R Micro 150 56 g -locking mechanism using -High cost around
Servo Linear Servo ball screw RM350
100mm 210:1 6 V -Large torque -Short stroke around 3
-Easily attach to robot cm to 10 cm only
body
-light 56g
-small in size
Table 3: List of DC Motors and Servo Motors
287