Page 158 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 158
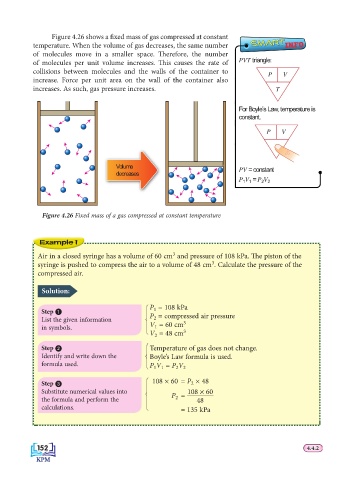
Figure 4.26 shows a fi xed mass of gas compressed at constant
SMART
temperature. When the volume of gas decreases, the same number SMART INFO
of molecules move in a smaller space. Th erefore, the number
of molecules per unit volume increases. Th is causes the rate of PVT triangle:
collisions between molecules and the walls of the container to P V
increase. Force per unit area on the wall of the container also
increases. As such, gas pressure increases. T
For Boyle’s Law, temperature is
constant.
P V
Volume PV = constant
decreases
P V = P V
2 2
1 1
Figure 4.26 Fixed mass of a gas compressed at constant temperature
Example 1
3
Air in a closed syringe has a volume of 60 cm and pressure of 108 kPa. Th e piston of the
3
syringe is pushed to compress the air to a volume of 48 cm . Calculate the pressure of the
compressed air.
Solution:
1
Step P = 108 kPa
P = compressed air pressure
List the given information 14243 2 3
1
in symbols. V = 60 cm 3
V = 48 cm
2
Step Temperature of gas does not change.
Identify and write down the 123
Boyle’s Law formula is used.
formula used. P V = P V
1 1
2 2
Step 108 × 60 = P × 48
2
Substitute numerical values into 14243 P = 108 × 60
the formula and perform the 2 48
calculations. = 135 kPa
152 4.4.2
152
4.4.2