Page 162 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 162
Charles’ Law states that volume is directly proportional Charles’ Law
to absolute temperature for a fi xed mass of gas at
constant pressure.
V ∝ T
V = kT http://bt.sasbadi.com/p4156
where k is a constant
T = absolute temperature (K)
SMART
3
V = volume of gas (m ) SMART INFO
V
As such, = k
T For Charles’ Law, pressure is
constant.
If a gas experiences a change in volume and temperature from
condition 1 to condition 2,
V
V V 1
since = k, condition 1 of gas: = k T
T T 1
V 2
condition 2 of gas: = k V
T 2 T = constant
V 1 V 2 V V
therefore, = 1 = 2
T 1 T 2 T 1 T 2
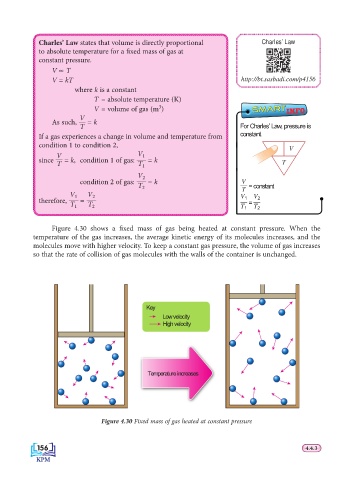
Figure 4.30 shows a fi xed mass of gas being heated at constant pressure. When the
temperature of the gas increases, the average kinetic energy of its molecules increases, and the
molecules move with higher velocity. To keep a constant gas pressure, the volume of gas increases
so that the rate of collision of gas molecules with the walls of the container is unchanged.
Key
Low velocity
High velocity
Temperature increases
Figure 4.30 Fixed mass of gas heated at constant pressure
156
156
156 4.4.3
4.4.3