Page 155 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 155
Immunology ` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS Immunology ` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS SECTIon II 111
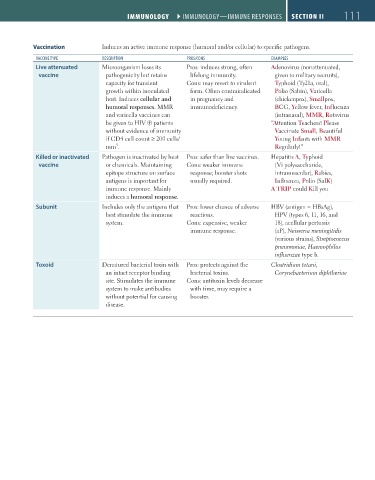
Vaccination Induces an active immune response (humoral and/or cellular) to specific pathogens.
VaccIne type deScrIptIon proS/conS eXampleS
Live attenuated Microorganism loses its Pros: induces strong, often Adenovirus (nonattenuated,
vaccine pathogenicity but retains lifelong immunity. given to military recruits),
capacity for transient Cons: may revert to virulent Typhoid (Ty21a, oral),
growth within inoculated form. Often contraindicated Polio (Sabin), Varicella
host. Induces cellular and in pregnancy and (chickenpox), Smallpox,
humoral responses. MMR immunodeficiency. BCG, Yellow fever, Influenza
and varicella vaccines can (intranasal), MMR, Rotavirus
be given to HIV ⊕ patients “Attention Teachers! Please
without evidence of immunity Vaccinate Small, Beautiful
if CD4 cell count ≥ 200 cells/ Young Infants with MMR
3
mm . Regularly!”
Killed or inactivated Pathogen is inactivated by heat Pros: safer than live vaccines. Hepatitis A, Typhoid
vaccine or chemicals. Maintaining Cons: weaker immune (Vi polysaccharide,
epitope structure on surface response; booster shots intramuscular), Rabies,
antigens is important for usually required. Influenza, Polio (SalK)
immune response. Mainly A TRIP could Kill you
induces a humoral response.
Subunit Includes only the antigens that Pros: lower chance of adverse HBV (antigen = HBsAg),
best stimulate the immune reactions. HPV (types 6, 11, 16, and
system. Cons: expensive, weaker 18), acellular pertussis
immune response. (aP), Neisseria meningitidis
(various strains), Streptococcus
pneumoniae, Haemophilus
influenzae type b.
Toxoid Denatured bacterial toxin with Pros: protects against the Clostridium tetani,
an intact receptor binding bacterial toxins. Corynebacterium diphtheriae
site. Stimulates the immune Cons: antitoxin levels decrease
system to make antibodies with time, may require a
without potential for causing booster.
disease.
FAS1_2019_02-Immunology.indd 111 11/7/19 3:24 PM