Page 156 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 156
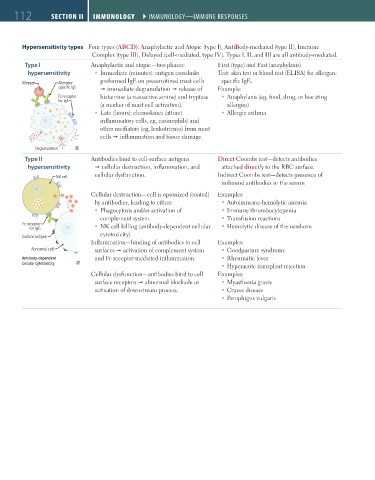
112 SECTIon II Immunology ` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS Immunology ` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS
Hypersensitivity types Four types (ABCD): Anaphylactic and Atopic (type I), AntiBody-mediated (type II), Immune
Complex (type III), Delayed (cell-mediated, type IV). Types I, II, and III are all antibody-mediated.
Type I Anaphylactic and atopic—two phases: First (type) and Fast (anaphylaxis).
hypersensitivity Immediate (minutes): antigen crosslinks Test: skin test or blood test (ELISA) for allergen-
preformed IgE on presensitized mast cells specific IgE.
Allergen Allergen-
specific IgE immediate degranulation release of Example:
Fc receptor histamine (a vasoactive amine) and tryptase Anaphylaxis (eg, food, drug, or bee sting
for IgE
(a marker of mast cell activation). allergies)
Late (hours): chemokines (attract Allergic asthma
inflammatory cells, eg, eosinophils) and
other mediators (eg, leukotrienes) from mast
cells inflammation and tissue damage.
Degranulation
Type II Antibodies bind to cell-surface antigens Direct Coombs test—detects antibodies
hypersensitivity cellular destruction, inflammation, and attached directly to the RBC surface.
cellular dysfunction. Indirect Coombs test—detects presence of
NK cell
unbound antibodies in the serum
Cellular destruction—cell is opsonized (coated) Examples:
by antibodies, leading to either: Autoimmune-hemolytic anemia
Phagocytosis and/or activation of Immune thrombocytopenia
complement system. Transfusion reactions
Fc receptor NK cell killing (antibody-dependent cellular Hemolytic disease of the newborn
for IgG
cytotoxicity).
Surface antigen
Inflammation—binding of antibodies to cell Examples:
Abnormal cell surfaces activation of complement system Goodpasture syndrome
Antibody-dependent and Fc receptor-mediated inflammation. Rheumatic fever
cellular cytotoxicity
Hyperacute transplant rejection
Cellular dysfunction—antibodies bind to cell Examples:
surface receptors abnormal blockade or Myasthenia gravis
activation of downstream process. Graves disease
Pemphigus vulgaris
FAS1_2019_02-Immunology.indd 112 11/7/19 3:24 PM